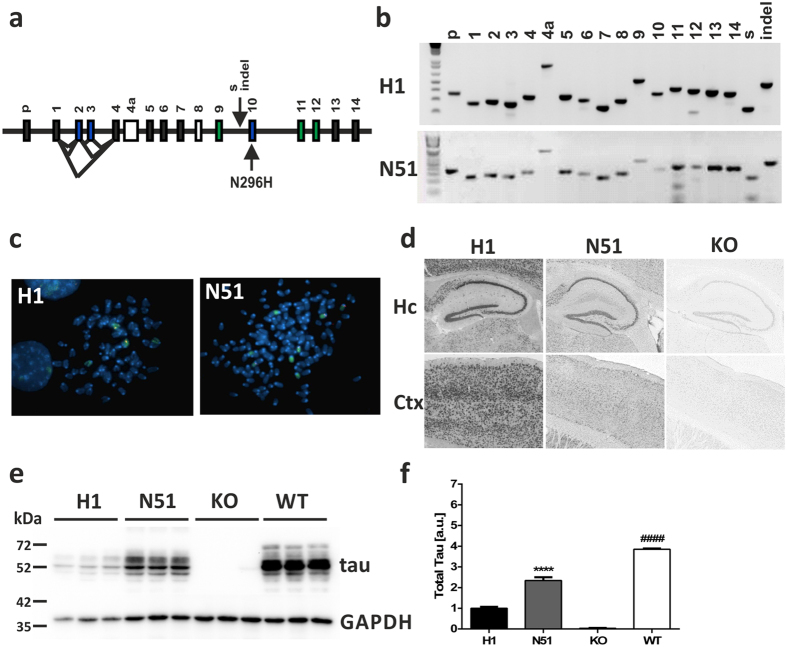
Figure 1. Generation of PAC-based tau transgenic mouse line expressing wild-type or N296H mutant human MAPT.
(a) Exon structure of the human MAPT genomic locus. p - promoter, s - Saitohin (STH) gene, indel - 238 bp insertion relative to H2 haplotype, black exons - constitutive expression, blue exons - alternatively spliced, white exons - not present in human CNS tau protein, green exons and exon 10 - microtubule binding domain. (b) Exon PCR for assessment of MAPT transgene integrity. All 16 exons were amplified as well as the Saitohin gene (s) nested between exons 9 and 10 and the 238 bp insertion (indel) that characterizes the H1 haplotype. (c) Localization of H1 wild-type and N51 mutant transgenes with chromosome paints by fluorescence in situ hybridization. A single integration transgene site (red) was confirmed for both H1 (chromosome 6, green) and N51 (chromosome 9, green) line. (d) MAPT transgene mRNA expression assessed by RNA in situ hybridization of H1 and N51 transgenic line compared to Mapt KO control. Hc: hippocampus; Ctx: cortex. (e) Tau transgene protein expression in whole brain extract of 3–5 month old H1 and N51 animals compared to Mapt KO nontransgenic littermates and C57BL6 animals with endogenous tau expression. (f) Quantification of expression levels normalized to GAPDH loading control. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc correction. Results represent mean signal ± SEM. ****p < 0.0001 (compared to H1), ####p < 0.0001 (compared to H1 and N51), N = 3 samples per group.