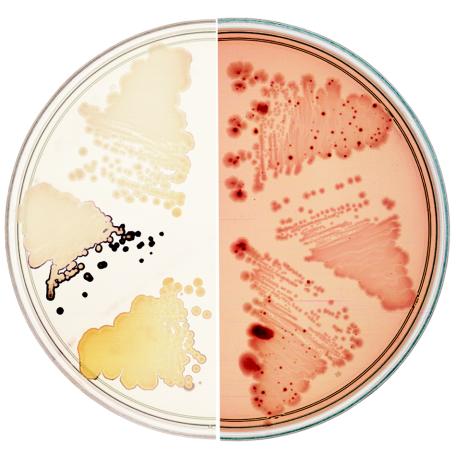
FIG. 3.
Two phenotypes of E. coli pgl mutants. (Left) pgl mutants accumulate starch and stain blue-black with iodine vapors when grown on minimal maltose plates, not seen for wild-type strains. (Right) Wild-type strains cannot utilize salicin as a C source but give rise to Bgl+ mutants that appear as dark red papillae on MacConkey-salicin plates, not seen in pgl mutants. Streaks of three different strains are shown on each plate. From the top and proceeding clockwise: wt (MG1655), a pgl mutant containing the control plasmid pJL6 (M2524), the pgl mutant containing the pgl+ plasmid pJL6-ybhE/pgl (M2526), MG1655, M2524, and M2526.