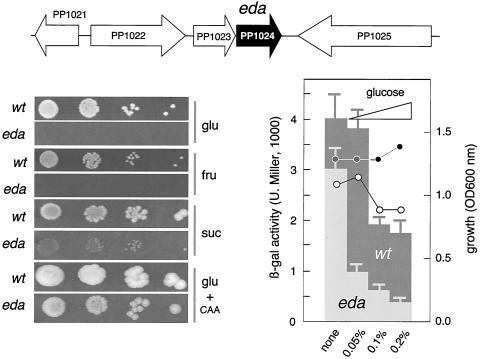
FIG. 5.
Phenotypes of an eda mutant of P. putida MAD2. The chromosomal region of the eda gene encoding 2-dehydro-3-deoxyphosphogluconate aldolase is shown at the top. Some of the adjacent ORFs encode somewhat related functions: PP1021 encodes the transcriptional regulator HexR, PP1022 determines glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, PP1023 encodes phosphogluconolactonase, and PP1025 corresponds to leuA, the gene for isopropylmalate synthase. The genomic context rules out any polar effect of the eda::xylE insertion. The plate assays at the lower left show the growth of the eda mutant on glucose (glu), fructose (fru), succinate (suc), and the combination of glucose plus amino acids (glu + CAA). Note the lack of growth on glucose and fructose, the poor growth on succinate, and the suboptimal development on CAA added with glucose. For the experiment shown at the lower right, Pu-lacZ reporter strain P. putida MAD2 and its eda derivative were subjected to a test of carbon Pu inhibition at various concentrations of glucose in MM-CAA as indicated (0.05%, ∼2.5 mM; 0.1%, ∼5 mM; 0.2%, ∼10 mM). The OD600 of the cultures grown for the same period of time is indicated, highlighting the noxious effect of glucose on the eda mutant. Note the poor expression of Pu in cells lacking eda as the glucose concentration in the medium increases. β-gal, β-galactosidase; U. Miller, Miller units; wt, wild type.