Figure 2.
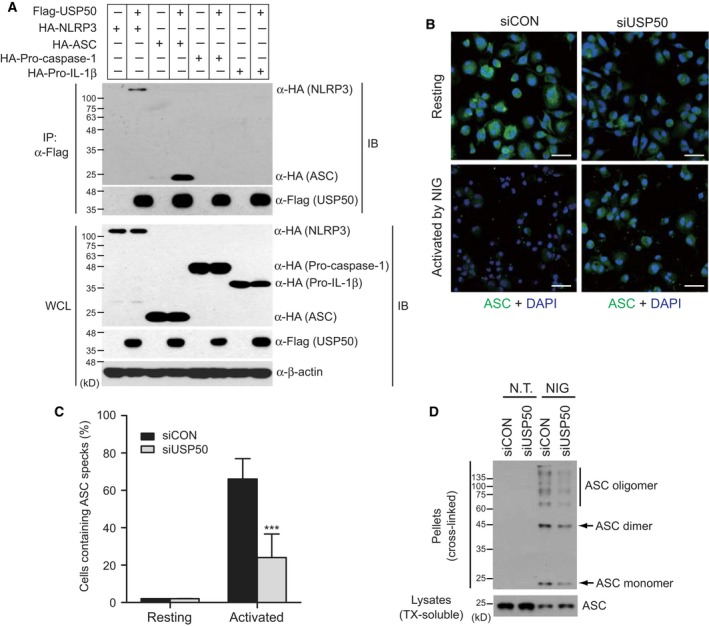
USP50 binds to the ASC protein and is required for ASC speck formation and oligomerization. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation assays to demonstrate the interaction of USP50 with the ASC protein. Plasmids encoding HA‐NLRP3, HA‐ASC, HA‐HA‐procasapase‐1 or HA‐pro‐IL‐1beta were transfected into HEK293 cells in the absence or presence of Flag‐tagged USP50 as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using Flag antibody. WCL and immunoprecipitates (IP) were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (B) THP‐1 cells, knocked down by siCON and siUSP50 pools, were untreated (upper panel, Resting) or treated (lower panel, Activated) with NIG (10 μm) for 1 h and subsequently immunostained by anti‐ASC and Alexa Fluor 488‐conjugated secondary antibodies, together with DAPI for nuclear stain. Images were acquired by laser scanning confocal microscopy. The images were merged, with ASC (green) and nucleus (blue). Scale bars, 50 μm. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (C) ASC speck‐forming cells were scored after NIG stimulation in two independent experiments. ASC specks were counted in five random areas of each image in duplicate experiments and described as a percentage of ASC specks for total cell nuclei. In each region, at least 200 cells were blindly counted. The data were statistically analyzed by a t‐test and show the mean ± SD. ***P < 0.001 compared to THP‐1 cells treated with a control siRNA pool. (D) ASC aggregation was analyzed by IB analysis in control THP‐1 and USP50‐knockdown THP‐1 cells. IB analysis for the ASC oligomerization assay was performed by anti‐ASC antibody in the pellets (cross‐linked by disuccinimidyl suberate) and soluble lysates (treated with TX) of THP‐1 cells, treated with or without NIG. The data are representative of three independent experiments. TX, Triton X‐100.
