Figure 4.
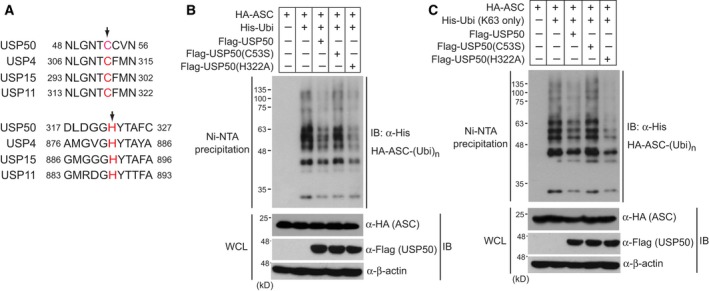
Catalytic inactive mutant of USP50 does not inhibit K63‐linked polyubiquitination of the ASC protein. (A) Putative amino acid residues critical for the deubiquitinating enzyme activity of USP50. The alignment of amino acid sequences of USP50 and other USP proteins shows that the Cys 53 and His 322 residues of USP50 are highly conserved. Arrow indicates the conserved residues tested in this experiment. (B) Plasmids encoding wild‐type His‐Ubi and HA‐ASC were cotransfected with plasmids encoding wild‐type Flag‐USP50, the Flag‐USP50(C53S) mutant or Flag‐USP50 (H322A) mutant into HEK293 cells. After cells were lysed under the denaturing conditions of 6 m guanidine‐HCl, Ni‐nitrilotriacetic acid‐mediated pull‐down assays were performed and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (C) Plasmids encoding His‐tagged K63 only ubiquitin mutant [His‐Ubi (K63 only)] and HA‐ASC were cotransfected with a plasmid‐encoding Flag‐USP50 or the above USP50 mutants into HEK293 cells. Ni‐nitrilotriacetic acid pull‐down assays were performed and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. The data for IB analysis are representative of at least three independent experiments.
