Figure 4.
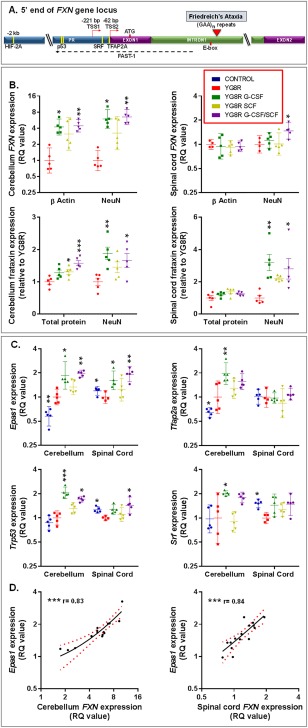
Both frataxin and regulatory factors implicated in controlling frataxin transcription are elevated in the cerebellum and spinal cord of YG8R mice treated with G‐CSF and/or SCF. (A) A schematic of the 5’ end of the human frataxin (FXN) gene showing approximate locations of the binding sites (yellow bars) for HIF‐2A, SRF, TFAP2A, and p53 in human or murine cells. The locations of the promotor (PR), Exon1, Exon2, and Intron1 regions are depicted. Different transcription start sites (TSS1 and TSS2) are shown upstream of Exon1, which holds the ATG translation start site. The directions of transcription for FXN (red arrows) and FXN antisense transcript (FAST‐1; dashed black arrow) are shown. The red triangle indicates the site of the trinucleotide GAA repeat expansion within intron 1 of FXN gene of patients with Friedreich's ataxia. The relative (B) mRNA and protein expression levels of frataxin within the cerebellum and spinal cord of YG8R mice (normalized to NeuN or β actin); (C) mRNA expression levels of transcription factors implicated in controlling frataxin expression Epas1, Srf, Tfap2a, and Trp53 (normalized to NeuN). (D) Correlation and linear regression analysis of FXN and Epas1 mRNA levels (normalized to NeuN) in the spinal cord and cerebellum of treated YG8R mice (lines of best fit and 95% confidence interval [CI] are depicted); r = Spearman's correlation coefficient. All statistical comparisons are versus YG8R mice. Comparisons between control and untreated YG8R mice were analyzed using unpaired t tests or Mann–Whitney U tests. For all other analyses, either one‐way analysis of variance followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test or Kruskal‐Wallis followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test was applied. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. For mRNA and protein expression, values represent the geometric means ± 95% CI and means ± standard error of the mean, respectively, relative to values in untreated YG8R mice. For all tests, n = 4 or 5 per genotype. mRNA = messenger RNA; NeuN = neuronal nuclear antigen; RQ = relative quantities.
