Figure 6.
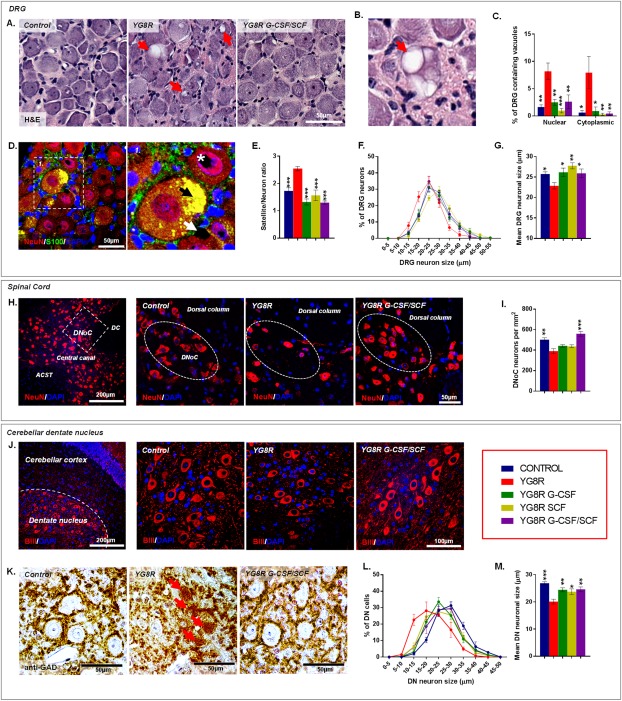
G‐CSF and SCF administration improves Friedreich's ataxia–associated pathology. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin–stained DRG depicting reductions in vacuolization (red arrows) of large sensory neurons within YG8R mice treated with G‐CSF/SCF. (B) High‐powered image of a DRG neuron showing significant vacuolisation (red arrow). (C) Frequency of DRG neurons containing nuclear or cytoplasmic vacuoles. (D) DRG sections labeled with NeuN and S100 showing autofluorescent lipofuscin (black arrow) and both intranuclear (white asterisk) and intracytoplasmic (white arrow) vacuolization. (E) DRG satellite‐to‐neuron cell ratio, (F) size range, and (G) mean cell size (diameter) of DRG neurons. (H) Images and (I) numbers of NeuN‐labeled neurons within the DNoC of YG8R mice treated with G‐CSF/SCF. (J) Images of beta‐3 tubulin‐expressing neurons and (K) grumose‐type GAD‐positive intracytoplasmic labeling pattern in and around the large neuronal cell bodies within the cerebellar dentate nucleus of control and YG8R mice. (L) Size range and (M) mean cell size (diameter) of beta‐3 tubulin‐labeled neurons within the cerebellar dentate nucleus. Comparisons between WT‐control and YG8R mice were compared using the unpaired t test. All other statistical comparisons are versus YG8R mice using either one‐way analysis of variance followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test or Kruskal‐Wallis followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; values represent means ± standard error of the mean. For all tests, n = 5 per genotype. ACST = anterior corticospinal tract; BIII = beta‐3 tubulin; DAPI = 4',6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; DC = dorsal column; DN = cerebellar dentate nucleus; DNoC = dorsal nucleus of Clarke; DRG = dorsal root ganglia; GAD = glutamate decarboxylase; G‐CSF = granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor; H&E = hematoxylin and eosin; NeuN = neuronal nuclear antigen; SCF = stem cell factor.
