Abstract
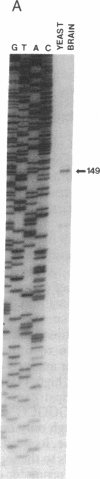
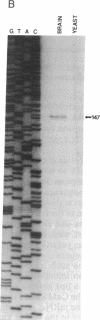
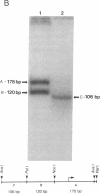
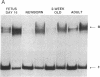
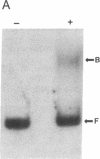
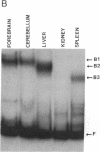
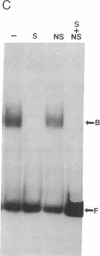
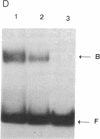
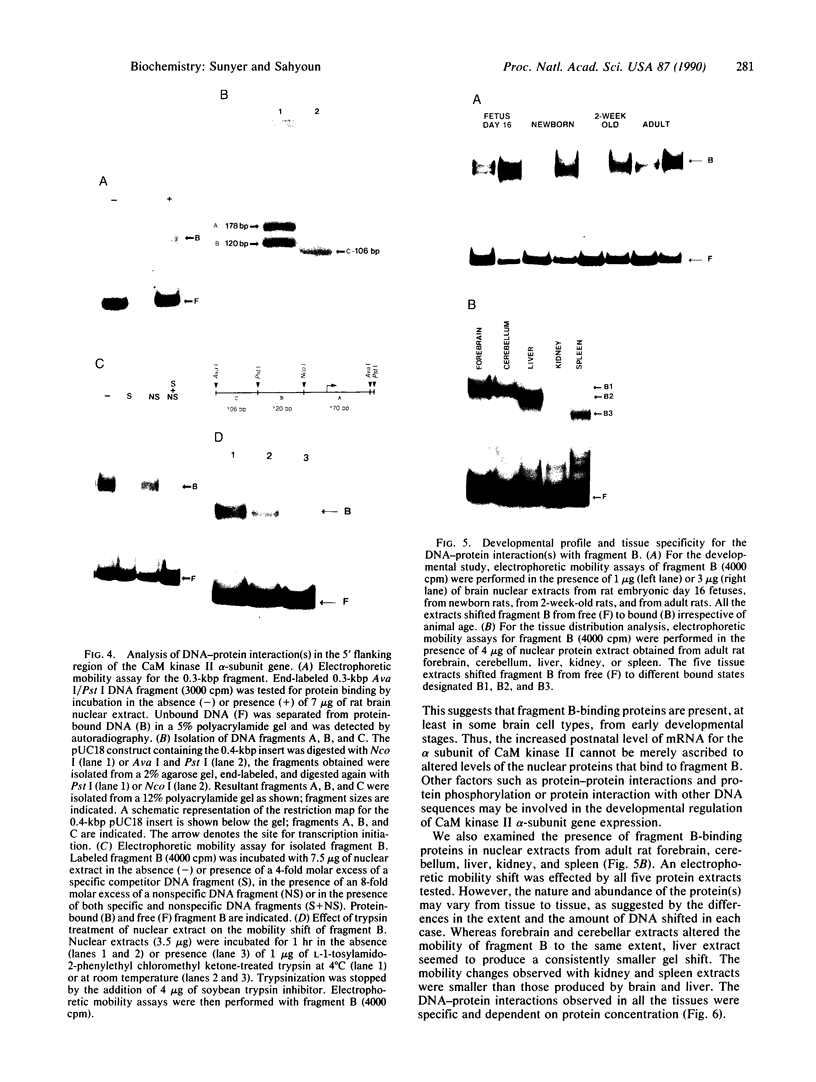
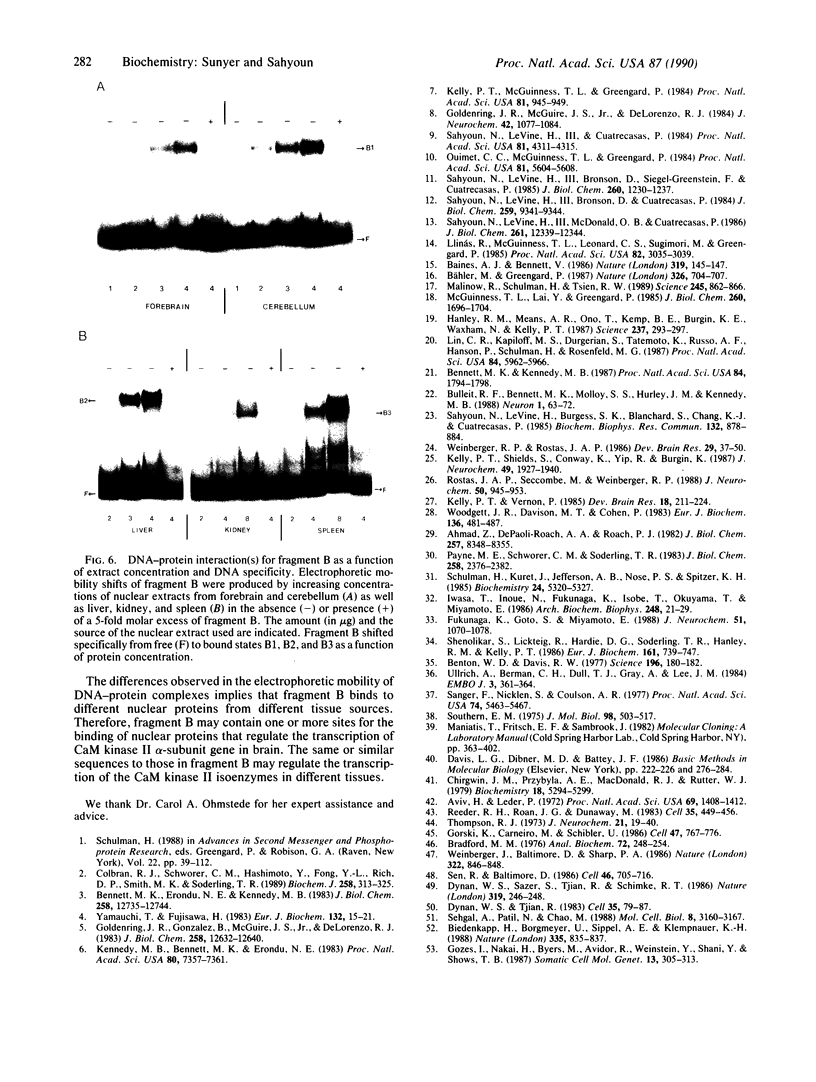
The 5' flanking region of the brain Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha-subunit gene was identified and characterized. A total of 430 bases was sequenced upstream from the translation initiation codon, and the site of transcription initiation was located at -149 or -147 bases as determined by primer extension and S1 nuclease protection analysis, respectively. TATA and CAAT boxes were absent from their standard positions; however, the 5' flanking region was rich in G + C and contained a GGGCG and a TATATAA sequence 76 and 160 bases upstream from the transcription initiation site, respectively. Moreover, the sequence CAACGG was found 85 and 146 bases upstream from this site, indicating presumptive binding sites for the Myb protein. Gel-mobility shift assays revealed that a 120-base-pair fragment, which included the G + C-rich, TATA, and CAACGG sequences bound nuclear proteins specifically. DNA-protein complexes with similar gel mobilities were obtained with nuclear extracts from rat forebrain or cerebellum and from neonatal or adult brains. Extracts from rat liver, kidney, and spleen generated specific DNA-protein complexes with different electrophoretic mobilities, suggesting the occurrence of different nuclear proteins that bind to 5' regulatory elements of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II alpha-subunit gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad Z., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Roach P. J. Purification and characterization of a rabbit liver calmodulin-dependent protein kinase able to phosphorylate glycogen synthase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8348–8355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines A. J., Bennett V. Synapsin I is a microtubule-bundling protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):145–147. doi: 10.1038/319145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Erondu N. E., Kennedy M. B. Purification and characterization of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that is highly concentrated in brain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12735–12744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Kennedy M. B. Deduced primary structure of the beta subunit of brain type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase determined by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1794–1798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulleit R. F., Bennett M. K., Molloy S. S., Hurley J. B., Kennedy M. B. Conserved and variable regions in the subunits of brain type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Neuron. 1988 Mar;1(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90210-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bähler M., Greengard P. Synapsin I bundles F-actin in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):704–707. doi: 10.1038/326704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbran R. J., Schworer C. M., Hashimoto Y., Fong Y. L., Rich D. P., Smith M. K., Soderling T. R. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):313–325. doi: 10.1042/bj2580313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Sazer S., Tjian R., Schimke R. T. Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):246–248. doi: 10.1038/319246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga K., Goto S., Miyamoto E. Immunohistochemical localization of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in rat brain and various tissues. J Neurochem. 1988 Oct;51(4):1070–1078. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenring J. R., Gonzalez B., McGuire J. S., Jr, DeLorenzo R. J. Purification and characterization of a calmodulin-dependent kinase from rat brain cytosol able to phosphorylate tubulin and microtubule-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12632–12640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenring J. R., McGuire J. S., Jr, DeLorenzo R. J. Identification of the major postsynaptic density protein as homologous with the major calmodulin-binding subunit of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J Neurochem. 1984 Apr;42(4):1077–1084. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gozes I., Nakai H., Byers M., Avidor R., Weinstein Y., Shani Y., Shows T. B. Sequential expression in the nervous system of c-myb and VIP genes, located in human chromosomal region 6q24. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Jul;13(4):305–313. doi: 10.1007/BF01534924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley R. M., Means A. R., Ono T., Kemp B. E., Burgin K. E., Waxham N., Kelly P. T. Functional analysis of a complementary DNA for the 50-kilodalton subunit of calmodulin kinase II. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):293–297. doi: 10.1126/science.3037704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasa T., Inoue N., Fukunaga K., Isobe T., Okuyama T., Miyamoto E. Purification and characterization of a multifunctional calmodulin-dependent protein kinase from canine myocardial cytosol. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Jul;248(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90396-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. T., McGuinness T. L., Greengard P. Evidence that the major postsynaptic density protein is a component of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):945–949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. T., Shields S., Conway K., Yip R., Burgin K. Developmental changes in calmodulin-kinase II activity at brain synaptic junctions: alterations in holoenzyme composition. J Neurochem. 1987 Dec;49(6):1927–1940. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb02456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. T., Vernon P. Changes in the subcellular distribution of calmodulin-kinase II during brain development. Brain Res. 1985 Feb;350(1-2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(85)90265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. B., Bennett M. K., Erondu N. E. Biochemical and immunochemical evidence that the "major postsynaptic density protein" is a subunit of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7357–7361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Kapiloff M. S., Durgerian S., Tatemoto K., Russo A. F., Hanson P., Schulman H., Rosenfeld M. G. Molecular cloning of a brain-specific calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5962–5966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., McGuinness T. L., Leonard C. S., Sugimori M., Greengard P. Intraterminal injection of synapsin I or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alters neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Schulman H., Tsien R. W. Inhibition of postsynaptic PKC or CaMKII blocks induction but not expression of LTP. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):862–866. doi: 10.1126/science.2549638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness T. L., Lai Y., Greengard P. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Isozymic forms from rat forebrain and cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1696–1704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouimet C. C., McGuinness T. L., Greengard P. Immunocytochemical localization of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5604–5608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne M. E., Schworer C. M., Soderling T. R. Purification and characterization of rabbit liver calmodulin-dependent glycogen synthase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2376–2382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roan J. G., Dunaway M. Spacer regulation of Xenopus ribosomal gene transcription: competition in oocytes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostas J. A., Seccombe M., Weinberger R. P. Two developmentally regulated isoenzymes of calmodulin-stimulated protein kinase II in rat forebrain. J Neurochem. 1988 Mar;50(3):945–953. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N., LeVine H., 3rd, Bronson D., Cuatrecasas P. Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in neuronal nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9341–9344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N., LeVine H., 3rd, Bronson D., Siegel-Greenstein F., Cuatrecasas P. Cytoskeletal calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Characterization, solubilization, and purification from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1230–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N., LeVine H., 3rd, Burgess S. K., Blanchard S., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Early postnatal development of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):878–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91889-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N., LeVine H., 3rd, Cuatrecasas P. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases from the neuronal nuclear matrix and post-synaptic density are structurally related. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4311–4315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N., LeVine H., 3rd, McDonald O. B., Cuatrecasas P. Specific postsynaptic density proteins bind tubulin and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12339–12344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H., Kuret J., Jefferson A. B., Nose P. S., Spitzer K. H. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase: broad substrate specificity and multifunctional potential in diverse tissues. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5320–5327. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal A., Patil N., Chao M. A constitutive promoter directs expression of the nerve growth factor receptor gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3160–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Lickteig R., Hardie D. G., Soderling T. R., Hanley R. M., Kelly P. T. Calmodulin-dependent multifunctional protein kinase. Evidence for isoenzyme forms in mammalian tissues. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 15;161(3):739–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J. Studies on RNA synthesis in two populations of nuclei from the mammalian cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1973 Jul;21(1):19–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb04222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Berman C. H., Dull T. J., Gray A., Lee J. M. Isolation of the human insulin-like growth factor I gene using a single synthetic DNA probe. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):361–364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01812.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Distinct factors bind to apparently homologous sequences in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):846–848. doi: 10.1038/322846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger R. P., Rostas J. A. Subcellular distribution of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity in rat cerebral cortex during development. Brain Res. 1986 Sep;394(1):37–50. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(86)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Davison M. T., Cohen P. The calmodulin-dependent glycogen synthase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Purification, subunit structure and substrate specificity. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Nov 15;136(3):481–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi T., Fujisawa H. Purification and characterization of the brain calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (kinase II), which is involved in the activation of tryptophan 5-monooxygenase. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 15;132(1):15–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]