Figure 3.
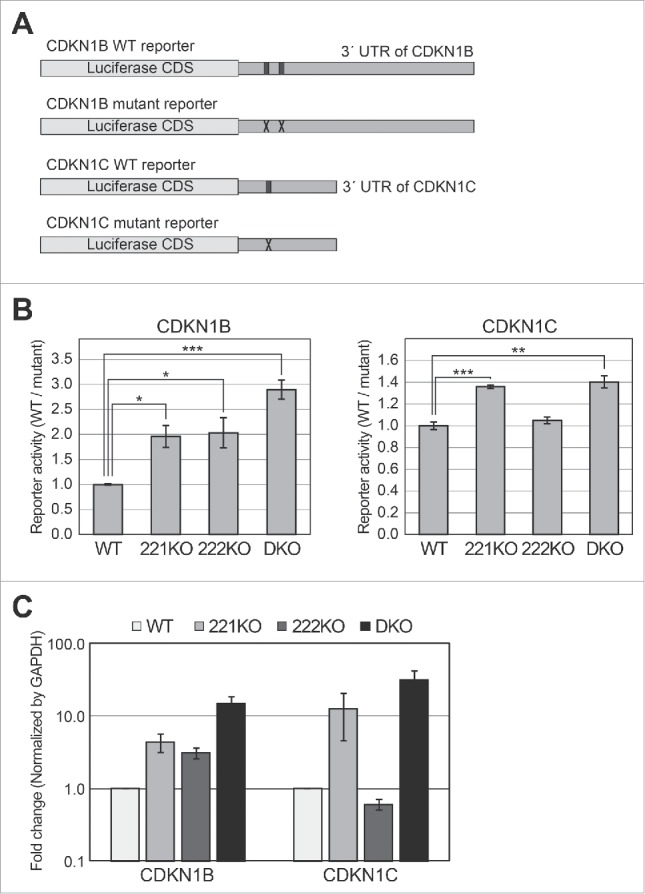
Reporter assays using targets of miR-221 and miR-222 in knockout cells. (A) Schematic representation of reporter constructs used in this experiment. The black boxes in the 3′ UTR of the wild type (WT) reporters indicate the binding sites of miR-221–3p and miR-222–3p. The ‘X’ marks in mutant reporters indicate the mutation introduced to block base-pairing between miRNAs and their target sites (Fig. S2). (B) Luciferase assays were performed using the CDKN1B and CDKN1C reporters. After the transfection of WT or mutant reporters into the cells, luciferase activity was measured. After normalizing the activity of the WT reporter by that of the mutant reporter, we compared the relative activities among wild type and knockout cells. Error bars show standard errors from four independent biologic replicates (n = 4). P values were calculated using a one-tailed t-test (*: P < 0.01, **: P < 0.001, ***: P < 0.0001). (C) Quantitative PCR experiments were performed to measure the mRNA levels of CDKN1B and CDKN1C in wild type and knockout cells, respectively. Error bars show standard errors from five independent biologic replicates (n = 5).
