Figure 1.
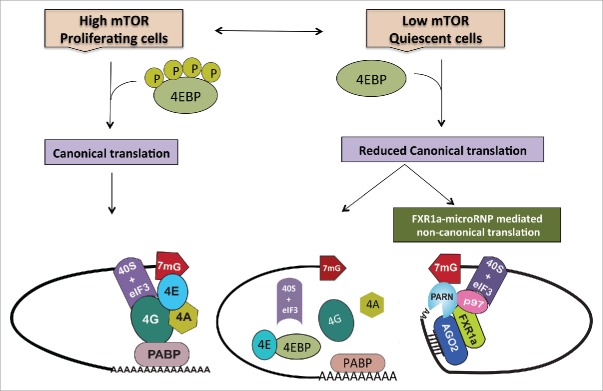
During normal proliferation, when mTOR kinase activity is high, cells depend on canonical cap dependent translation for global protein synthesis. However, under specific conditions such as quiescence, canonical protein synthesis is reduced due to low mTOR activity that causes dephosphorylation and thereby, activation of 4EBPs. Activated 4EBPs inhibit canonical cap dependent translation by binding eIF4E (the canonical cap binding protein) and preventing its interactions with eIF4G. In order to maintain the cellular state, cells operate alternative translation mechanisms to express specific genes. In quiescence, apart from low mTOR activity and 4EBP dephosphorylation—in certain cell lines and in immature oocytes where FXR1 levels are increased—a specialized FXR1a-microRNP complex mediates one such alternative mechanism. Similar to the conventional repressive microRNP, FXR1a-microRNP contains AGO2 and microRNAs but lacks the canonical microRNP repression effector, GW182. Instead, in FXR1a-microRNP, AGO2 interacts with a specific spliced isoform of the RNA binding protein FXR1a that does not participate in microRNA mediated repression142,143 and promotes specific mRNA translation.17,29,30 MicroRNA bound AGO2 directs recruitment of the complex to 3′UTRs. Poly (A) tails are decreased in these low mTOR conditions to avoid binding PABP that can recruit GW182 and promote microRNA-mediated deadenylation and repression. Increased deadenylation is brought about by PARN deadenylase in G0 cells, which is attributed to increased cap binding by PARN in G0.65 FXR1a-microRNP interacts with p97/DAP5, a non-canonical translation factor that brings in eIF3–40S ribosome subunit in place of eIF4G.103-113 FXR1a-microRNP also interacts with PARN that binds mRNA 5′ caps in G0 in place of eIF4E, thus connecting p97-FXR1a-microRNP that is recruited to the 3′ UTR, with the 5′cap to replace the canonical 5′-3′ eIF4E-eIF4G-PABP link.31 These alternate cap binding and ribosome recruitment factors promote specialized translation of specific poly(A) shortened mRNAs associated with FXR1a-microRNP in quiescent conditions, where canonical translation is reduced.