Figure 2.
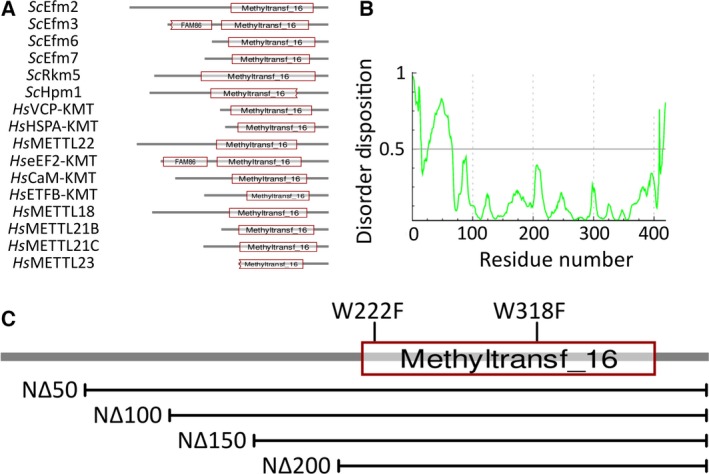
Efm2 has a long, partially disordered N‐terminal region separate from the core methyltransferase domain. (A) The domain architectures of all known Family 16 methyltransferases from yeast and human. A number of them have extended N‐terminal regions; Efm2 has the longest of all. Methyltransferase lengths are to scale; Efm2 is 419 residues long. Jagged edges of domains represent partial truncations. (B) The predicted disorder of Efm2 as determined by pondr‐fit. Disorder disposition > 0.5 represents disorder. (C) Mutagenesis of Efm2. Four N‐terminal truncation mutants and two point mutants were generated in order to characterise the N‐terminal region and the conserved tryptophans in Efm2. Note that all four N‐terminal truncations retain the core Family 16 methyltransferase domain.
