Figure 3.
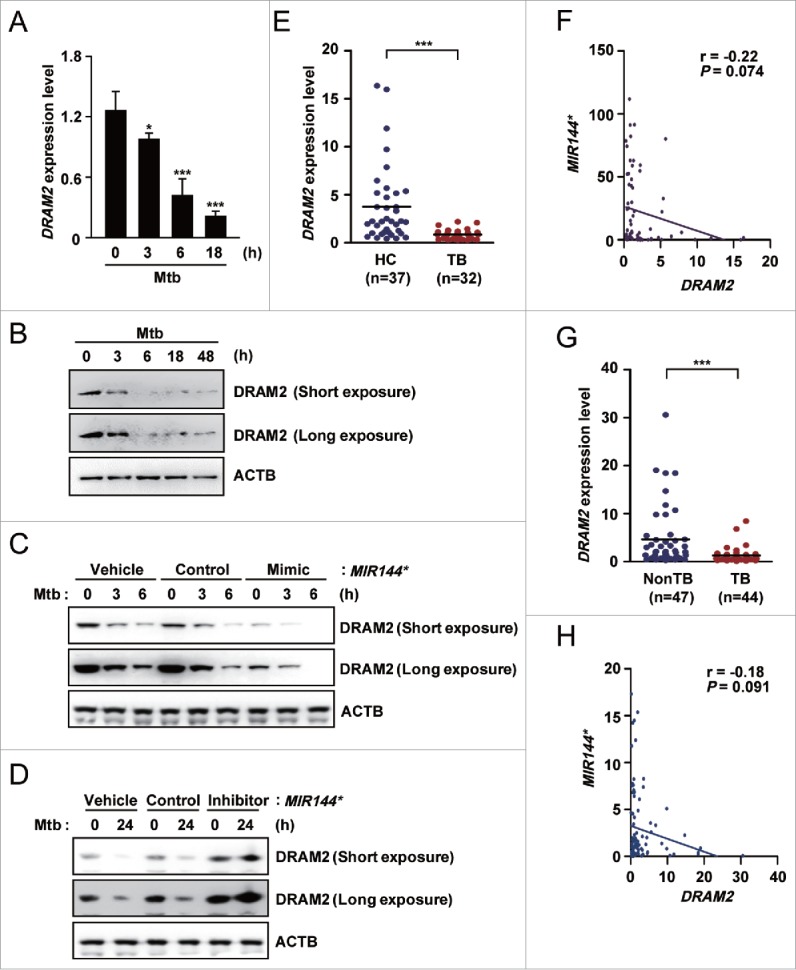
DRAM2 expression is downregulated by Mtb infection in human macrophages and in disease samples from tuberculosis patients. (A and B) Human MDMs infected with Mtb (MOI of 10) for the indicated times. (A) DRAM2 mRNA levels were determined by real-time PCR. (B) DRAM2 protein levels were evaluated by immunoblotting. (C and D) Human MDMs were transfected with vehicle control; mimic negative control or MIR144* mimic (50 nM for C); inhibitor negative control or MIR144* inhibitor (150 nM for D) for 24 h and then infected with Mtb for 3, 6 (C) or 24 h (D). DRAM2 protein levels were then determined by immunoblotting. (E) Human PBMCs were isolated from HCs (n = 37) and TB patients (n = 32). Expression levels of DRAM2 were determined by real-time PCR. (F) Correlation of the expression of MIR144* and DRAM2 by Pearson regression in PBMCs from HCs and TB patients (Pearson r = −0.22, P = 0.074). (G) Real-time PCR analysis of DRAM2 expression in disease sites from nonTB controls (NonTB; n = 47) and disease sites from pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB patients (TB; n = 44). (H) Correlation of MIR144* and DRAM2 expression by Pearson regression in tissues from HCs and TB patients (Pearson r = −0.18, P = 0.091). Experiments were performed 3 times, and data are presented as means ± SD. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001, compared with untreated control (A). TB, tuberculosis patients; HCs, healthy controls.
