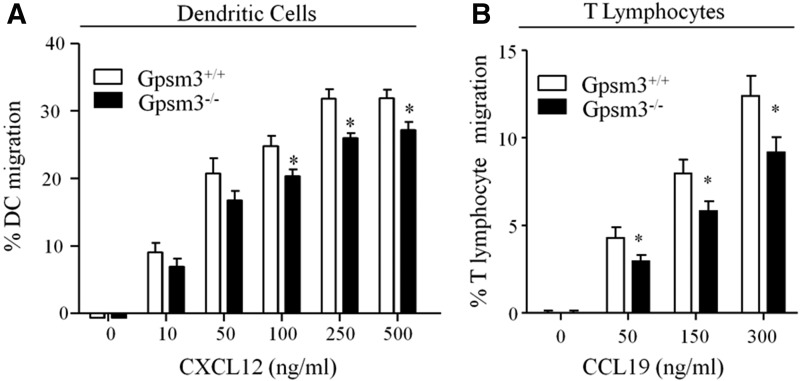
Fig. 4.
Loss of AGS4 results in defective chemotaxis in primary leukocytes. (A) Bone marrow–derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) from WT and AGS4/Gpsm3-null mice were prepared as described in Materials and Methods. BMDCs were loaded in transwell migration chambers with the bottom chamber containing serum-free RPMI in the absence and presence of 10, 50, 100, 250, and 500 ng/ml CXCL12 as indicated. After 20 hours at 37°C, cells in the bottom chamber were counted, and the percentage of cells migrated was calculated relative to the input where the number of cells migrating to vehicle only was subtracted. Data are represented as the mean ± S.E. of a minimum four independent experiments with at least triplicate determinations (*P < 0.01). (B) T lymphocytes were isolated from freshly harvested splenocytes of WT and AGS4/Gpsm3-null mice after red blood cell lysis and filtering to remove cell and tissue aggregates as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were loaded in transwell migration chambers with bottom chambers containing serum-free RPMI in the absence or presence of 50, 150, and 300 ng/ml CCL19. After 5 hours at 37°C, cells in the bottom chamber were counted, and the percentage of cells migrated was calculated relative to the input where the number of cells migrating to vehicle only was subtracted. Data are represented as the mean ±S.E. of at a minimum of four independent experiments with at least triplicate determinations (*P < 0.01).