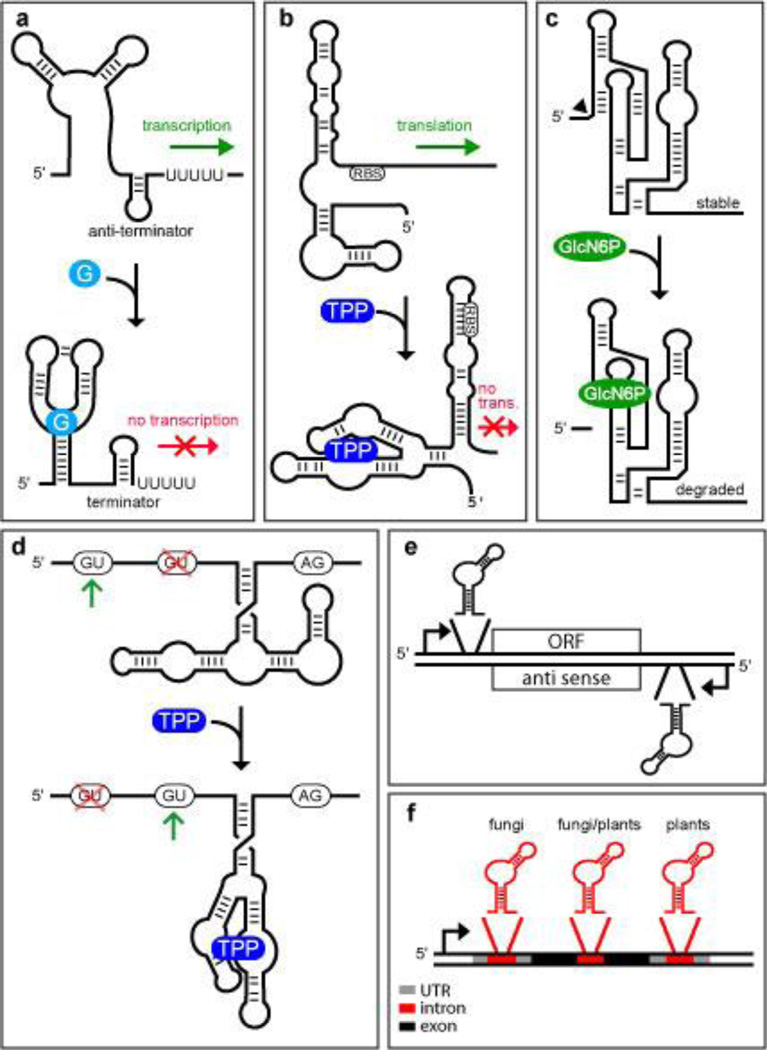
Figure 1.
Natural Riboswitch Locations and Mechanisms. (a) Transcription regulation based on a guanine-sensing riboswitch.121 When guanine (G) binds, the folding pathway favors the formation of a terminator stem at the expense of antiterminator stem formation. This architecture yields ‘off’ switch function because guanine causes transcription to terminate before the coding region of the mRNA is synthesized. Less common are examples of ‘on’ switch function where ligand binding favors antiterminator stem formation, as is observed with a related adenine-sensing riboswitch.122 (b) Translational regulation based on a TPP riboswitch.51 In the absence of the riboswitch ligand, expression of the down stream gene is permitted because translation can be initiated at the ribosomal binding site (RBS). However, in the presence of the ligand, the RNA adopts an alternate conformation that does not permit translation to be initiated at the RBS.123 (c) Metabolite-triggered ribozyme regulation of gene expression by GlcN6P riboswitches. When the ribozyme cofactor GlcN6P is low in concentration, the ribozyme does not undergo efficient self-cleavage and the stable mRNA can be translated. When GlcN6P is bound by the RNA, the ribozyme undergoes efficient self-cleavage, and the 3′ cleavage fragment including the ORF is rapidly degraded by a nuclease.57 (d) Control of alternative splicing by a TPP-sensing riboswitch in eukaryotes. When TPP concentrations are low, nucleotides from the unoccupied aptamer base pair near the second 5′ splice site, forcing the spliceosome to use the first 5′ splice site. When TPP is bound, the nucleotides formerly blocking the splice site are now involved in binding the ligand. This allows the spliceosome to choose the second 5′ splice site to yield an alternatively spliced mRNA. In fungi, ligand binding yields an alternatively spliced mRNA lacking upstream open reading frames (uORFs) that otherwise would decoy the ribosome from initiating translation at the main ORF.61 (e) Eubacterial riboswitch placement. Most riboswitches found in eubacteria are present within the 5′ untranslated regions (UTR) of mRNAs and directly control expression of a downstream open reading frame (ORF). There is bioinformatics evidence that at least one riboswitch controls the expression of an antisense RNA to regulate protein expression from a separate mRNA indirectly.53 (f) Eukaryotic riboswitch placement. Riboswitches have been found in introns located within the 5′ UTRs, coding regions, and 3′ UTRs of eukaryotic mRNAs.