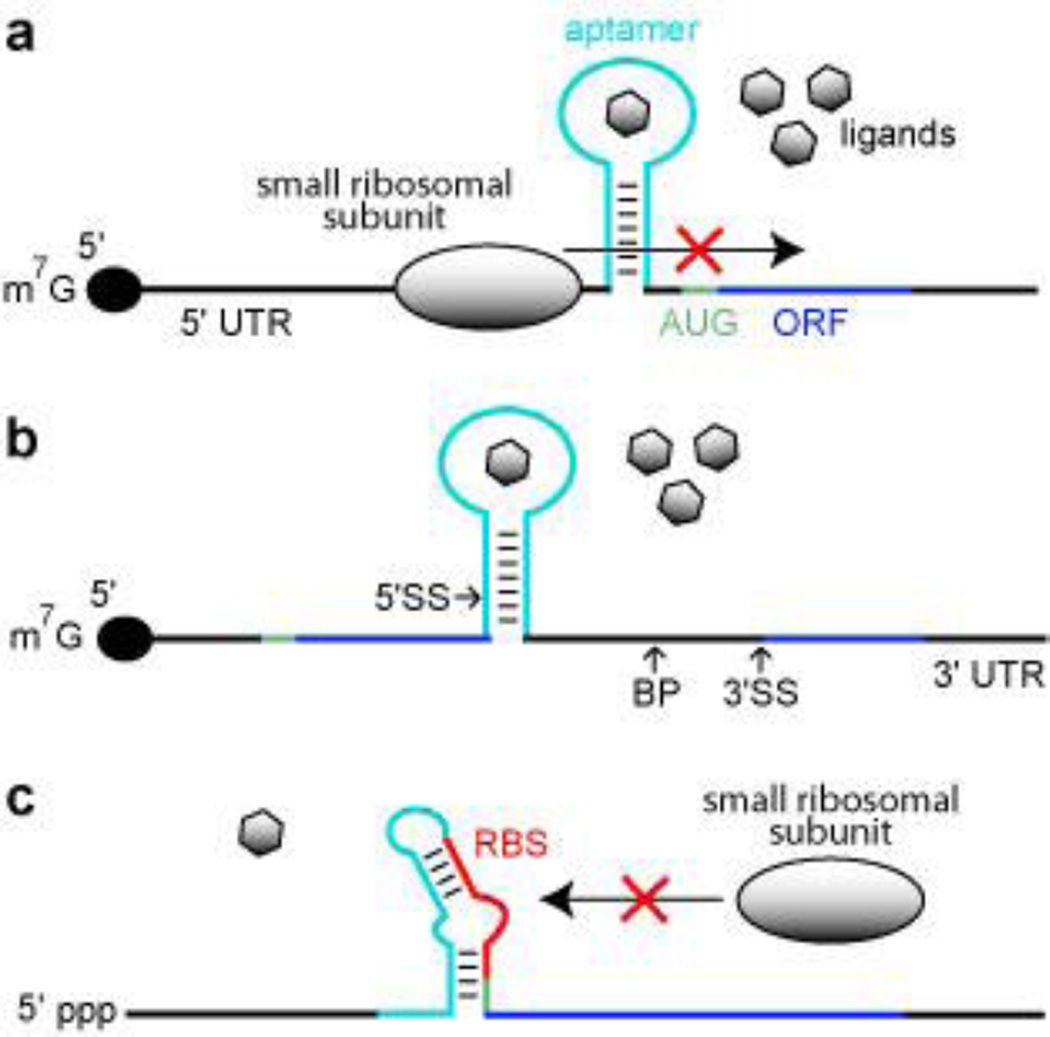
Figure 2.
Aptamer-based synthetic riboswitches. (a) Aptamer-mediated inhibition of ribosomal scanning in S. cerevisiae. Ligand binding by the aptamer stabilizes a structure within the 5′ UTR that precludes the ribosome from reaching the AUG start codon. Black lines represent UTRs, green line represents the start codon, dark blue line identifies the ORF, and the light blue line represents the aptamer domain. (b) Aptamer mediated inhibition of mRNA splicing in S. cerevisiae. Ligand binding stabilizes a structure that sequesters the 5′ splice site (5′ SS), which precludes efficient splicing. BP and 3′ SS designate the branch point and the 3′ splice site, respectively. Additional annotations are as described in a. (c) Aptamer mediated inhibition of ribosome binding in E. coli. The absence of ligand binding allows the aptamer sequence to base pair with the ribosome binding site (RBS), which inhibits ribosome binding. Annotations are as described in a.