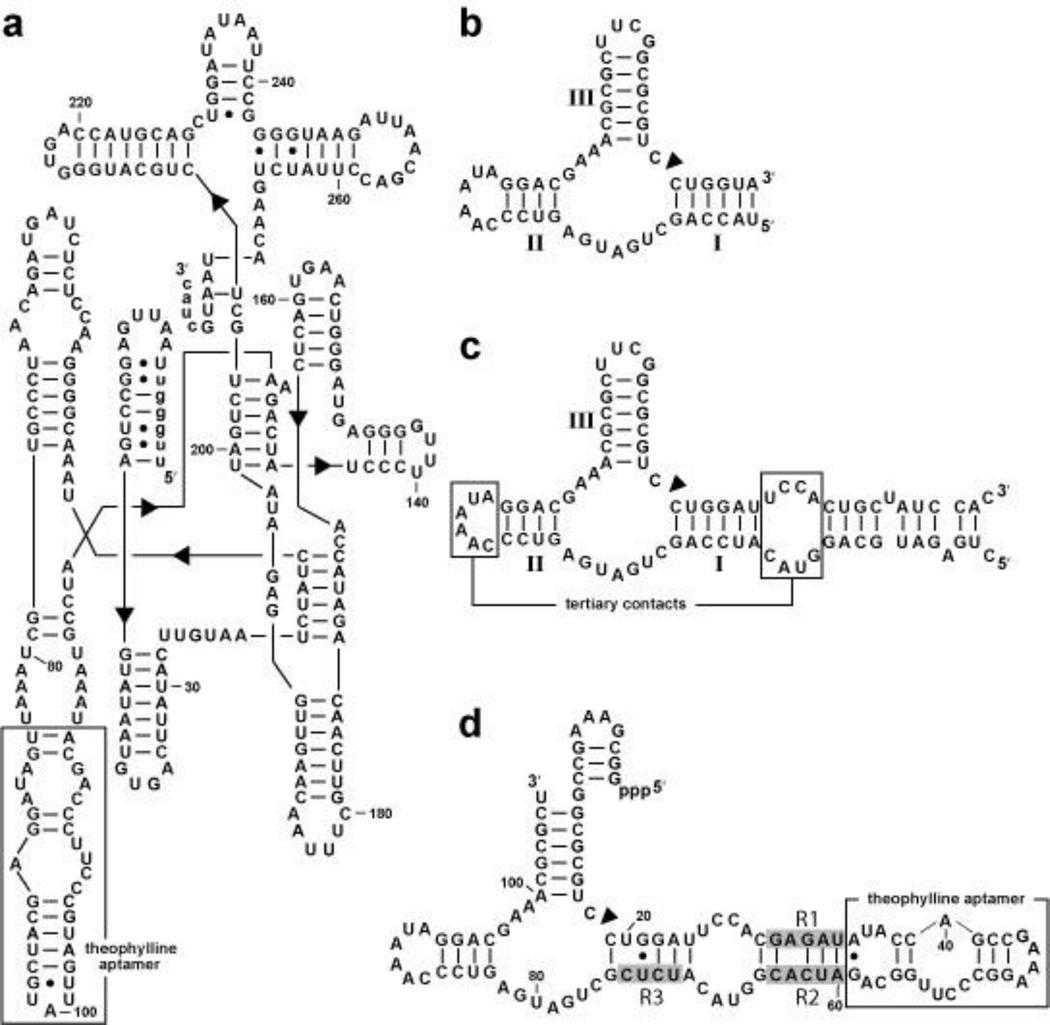
Figure 4.
Allosteric ribozymes as catalytic platforms for synthetic riboswitches. (a) Sequence and secondary structure model of an allosteric group I intron (Th2P6).32 Uppercase and lowercase letters identify intron and exon sequences, respectively. (b) A sequence encompassing only the minimal catalytic core of a hammerhead ribozyme with stems I through III identified. (c) Sequence and secondary structural model of the full-length Schistosoma mansoni hammerhead ribozyme.124 A construct based on this ribozyme is known to function in vivo.98 (d) Sequence and secondary structural model of a high-speed allosteric hammerhead ribozyme derived from the parental ribozyme in c. R1 through R3 (shaded nucleotides) were derived by in vitro selection from random-sequence domains. Theophylline binding is expected to permit the RNA to form tertiary contacts between the accessory domains in stems I and II and thereby exhibit high ribozyme activity.