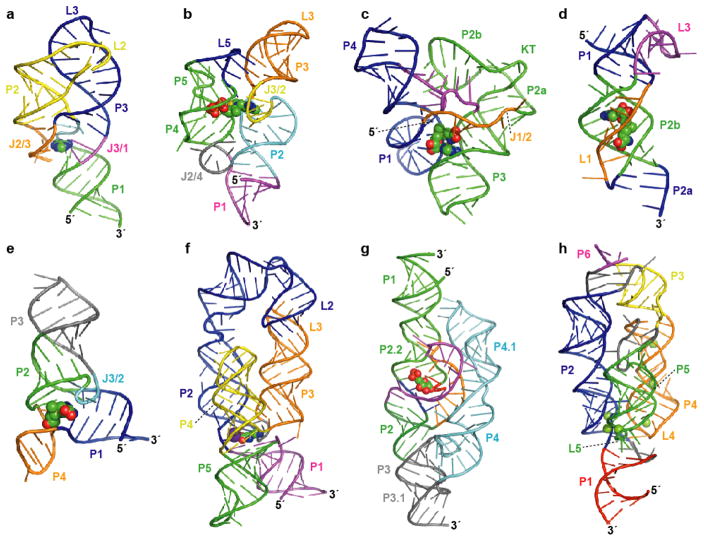
Figure 1.
Atomic resolution structures for representatives of eight riboswitch aptamer classes. Aptamer structure models are shown as ribbon diagrams and ligands are represented as spheres. Pairing elements and joining regions are indicated. (a) The purine riboswitch aptamer (PDB ID 1Y26, 1Y27, 1U8D) (22, 23). (b) The TPP riboswitch aptamer (PDB ID 2GDI, 2HOJ, 2CKY) (32–34). (c) The SAM-I riboswitch aptamer (PDB ID 2GIS) (44); KT, kink-turn. (d) The SAM-II riboswitch aptamer (PDB ID 2QWY) (45). (e) The SAM-III/SMK riboswitch aptamer (PDB ID 3E5C) (46). (f) The lysine riboswitch aptamer (PDB ID 3D0U, 3DIL) (56, 57); a specifically bound K+ ion (57) is depicted as a purple sphere. (g) The GlcN6P-responsive glmS ribozyme (PDB ID 2HO7, 2N74) (65, 66). (h) The Mg2+-responsive M-box riboswitch aptamer (PDB ID 2QBZ) (75); six crystallographically observed Mg2+ ions are shown.