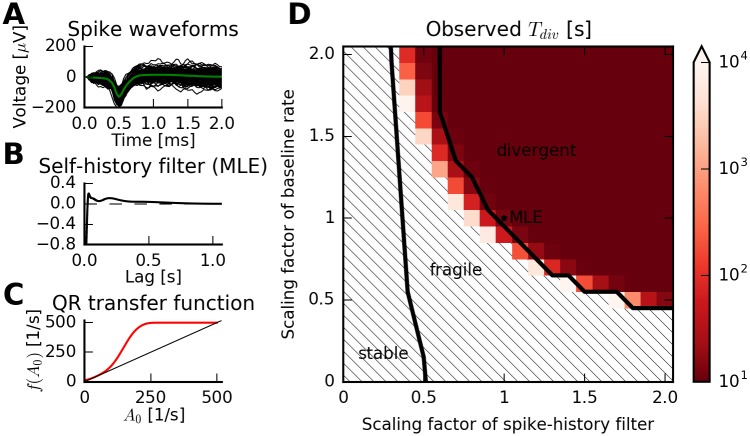
Fig 9. The quasi-renewal approximation predicts stability for complex (physiologically plausible) model parameters.
(A) Single-unit activity (SUA) from multi-electrode recordings from monkey cortical area PMv [31] (same unit as in Fig 2C). Spike waveforms are shown (mean waveform in green) and indicate well-sorted SUA. (B) Estimated spike-history kernel using maximum-likelihood estimation. The kernel exhibits a relative refractory period followed by an excitatory rebound. (C) The transfer function predicted by the QR approximation. There is a single stable fixed point at ≈ 500 s−1. The model is therefore classified as “divergent”. (D) The QR approximation predicts the maximum-likelihood estimate (MLE) (center dot) to be divergent. Color indicates average divergence times in simulations for variations of the baseline rate c (y-axis) and scaled versions of the filter relative to the integral of eη(s) − 1 (x-axis). Thick lines indicate the separation between areas for which the QR approximation predicts stability, fragility, or divergence. Overall, estimated divergence times from simulations agree with the qualitative predictions.