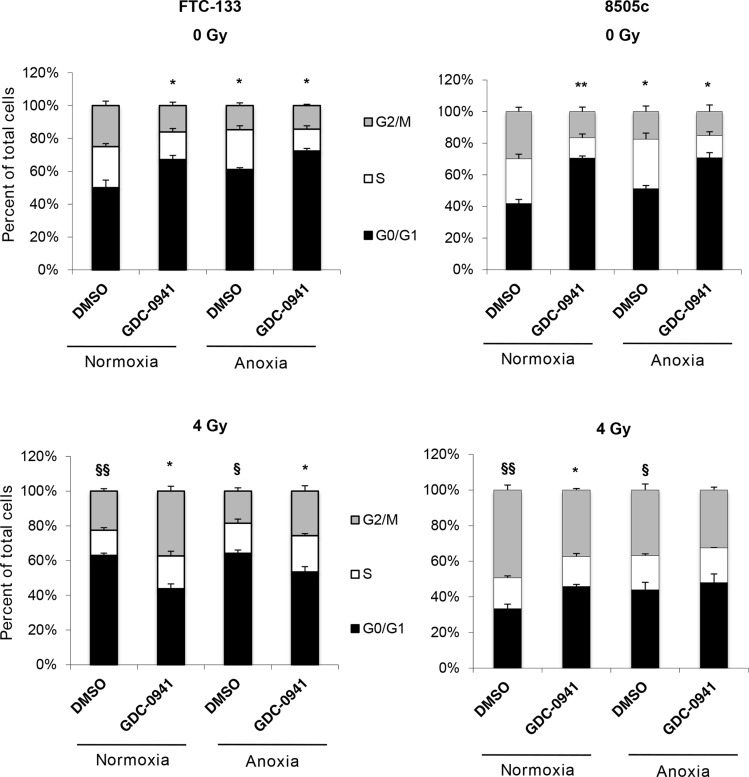
Figure 7. GDC-0941 abrogates radiation-mediated effects on cell cycle.
In un-irradiated cell lines, GDC-0941 and anoxia independently increased percentage cells in G0/G1 (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Radiation had differential effects across cell lines; significantly increasing percentage cells in G0/G1 (FTC-133) and G2/M (8505c) under normoxia and anoxia (§p < 0.05, §§p < 0.01). In irradiated FTC-133 cells, GDC-0941 significantly reduced percentage cells in G0/G1 under normoxia and anoxia (*p < 0.05). In irradiated 8505c cells, GDC-0941 significantly reduced percentage cells in G2/M under normoxia (*p < 0.05), with similar affects observed in anoxia. As for the clonogenic assays, FTC-133 and 8505c cells were incubated under normoxia/anoxia for 18 h with DMSO or 10 μM GDC-0941 and irradiated (4 Gy) in the specified conditions. Samples remained in the specified conditions for 24 h post irradiation, but instead of seeding for clonogenicity, samples were fixed and cell cycle distribution was assessed by flow cytometry analysis of propidium iodide stained cells. Data represents the mean ± S.E.M. of 3 independent experiments.