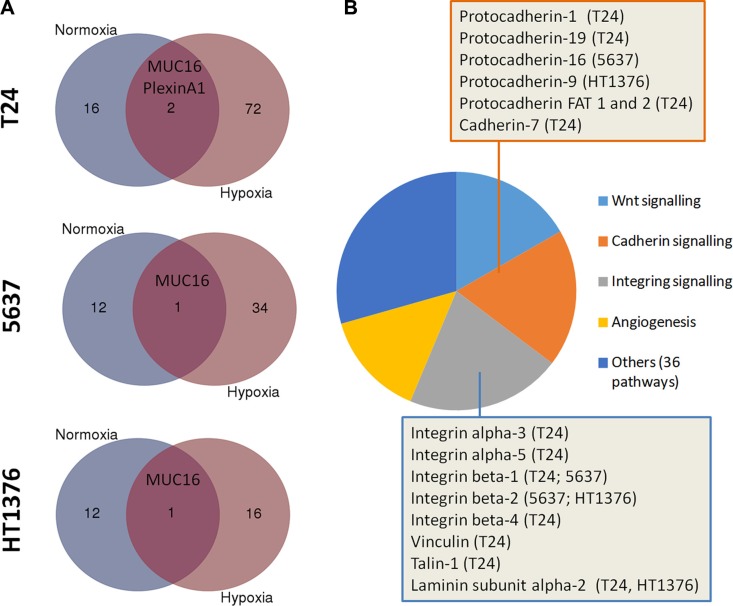
Figure 4.
(A) Number of putative STn-expressing glycoproteins identified by VVA lectin affinity-nanoLC tandem ESI-MS in normoxic and hypoxic cells. Briefly, proteins isolated from T24, 5637 and HT1376 cell lines in normoxia and hypoxia were digested with α-neuraminidase, which removes the sialic acid from STn exposing the Tn antigen. The samples were then enriched for Tn-expressing glycoproteins by VVA affinity chromatography and identified by nanoLC tandem ESI-MS. Since the Tn antigen was not detected in the original samples (before neuraminidase treatment) by both western blot and flow cytometry, it is likely that the glycoproteins identified by this approach may yield the STn antigen. Accordingly, a higher number of putative STn-expressing glycoproteins were present in hypoxic cells in comparison to normoxia. Interestingly, MUC16 was the only glycoprotein common to all cells and conditions. (B) Main signalling pathways associated with STn-expressing glycoproteins in hypoxia. Over 35% of the identified glycoproteins were associated with integrin or cadherin signalling pathways, as highlighted in the Figure. Other key oncogenic pathways also included Wnt signalling and angiogenesis. The STn antigen was also found in glycoproteins involved in other 36 molecular functions, highlighting the broad span of biological roles of STn expressing glycoproteins.