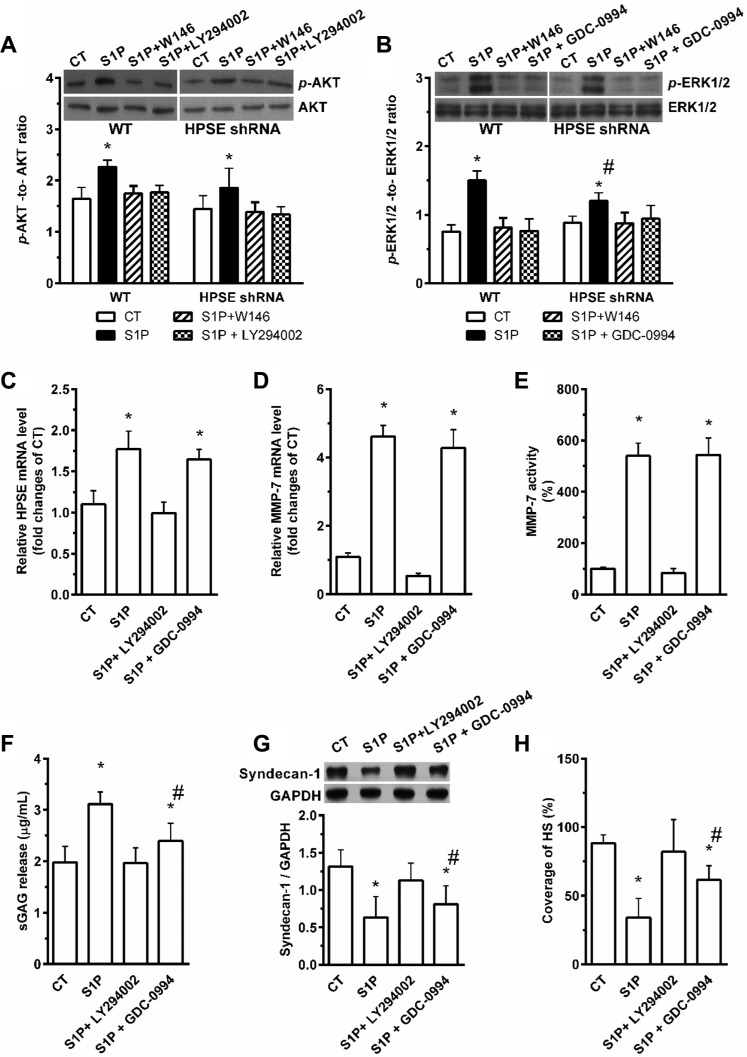
Figure 5. Involvement of PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2 pathways in S1P- S1P1-induced shedding and -suppressed the synthesis of syndecan-1.
HepG2 WT and HPSE shRNA cells were stimulated with 2 μM S1P for 72 h with or without pretreatment for 30 min with S1P1 inhibitor W146 (10 μM), PI3K/AKT inhibitor LY294002 (20 μM) or ERK1/2 inhibitor GDC-0994 (50 μM). (A) and (B), the phosphorylation levels of AKT (A) and ERK1/2 (B) in WT and HPSE shRNA cells were evaluated by Western blot. Histograms show densitometric quantification of p-AKT or p-ERK normalized to total AKT or ERK, respectively. (C) LY294002 inhibited the S1P-induced expression of HPSE mRNA, but GDC-0994 did not. (D) and (E) LY294002 abolished the S1P-induced mRNA expression and activity of MMP-7, but GDC-0994 did not. The mRNA expression of MMP-7 in cell lysates was performed by qRT-PCR, and the activity of MMP-7 in cell mediums was determined by using SensoLyte 520 MMP-7 assay kit (AnaSpec). (F) S1P-induced sGAG release was blocked by LY294002 or in partly inhibited by GDC-0994. sGAG in culture medium was detected by DMMB assay. (G) and (H), effects of S1P in the suppression of syndecan-1 expression (G) and decrease in the coverage of HS (H) were blocked by LY294002 or in partly inhibited by GDC-0994. Syndecan-1 expression was measured by Western blot. The coverage of heparan sulfate (HS) was estimated by using maximum-intensity projections of a confocal z-stack. *P < 0.05 as compared with WT control cells; #P < 0.05 as compared with S1P-treated WT control (ANOVA).