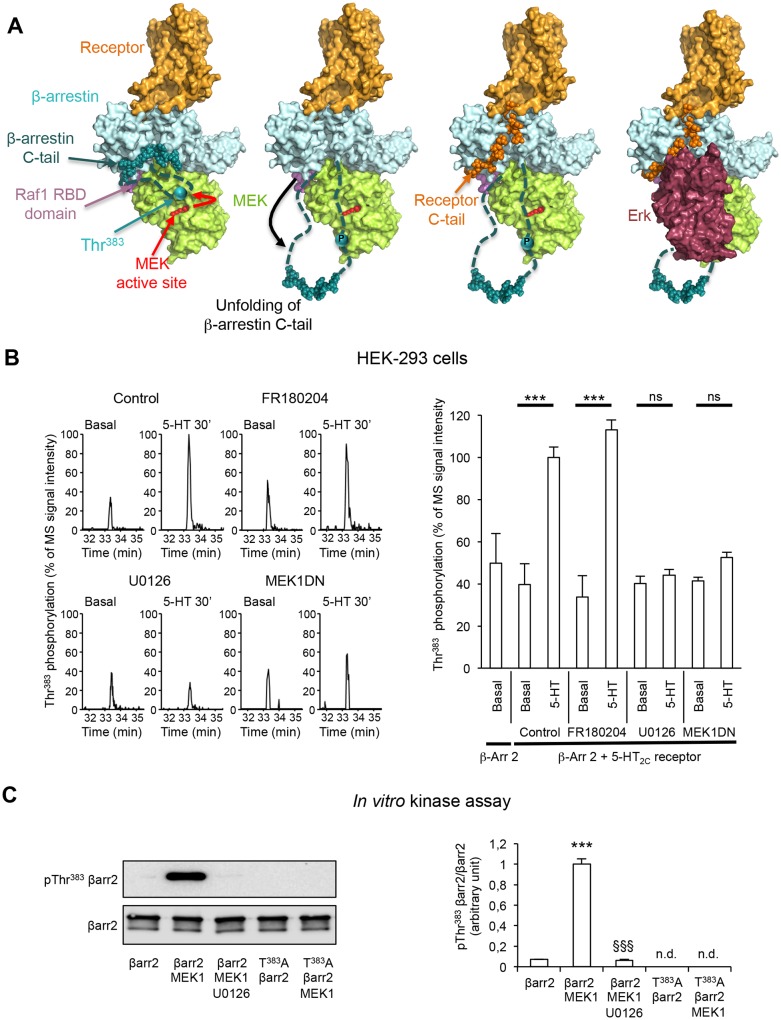
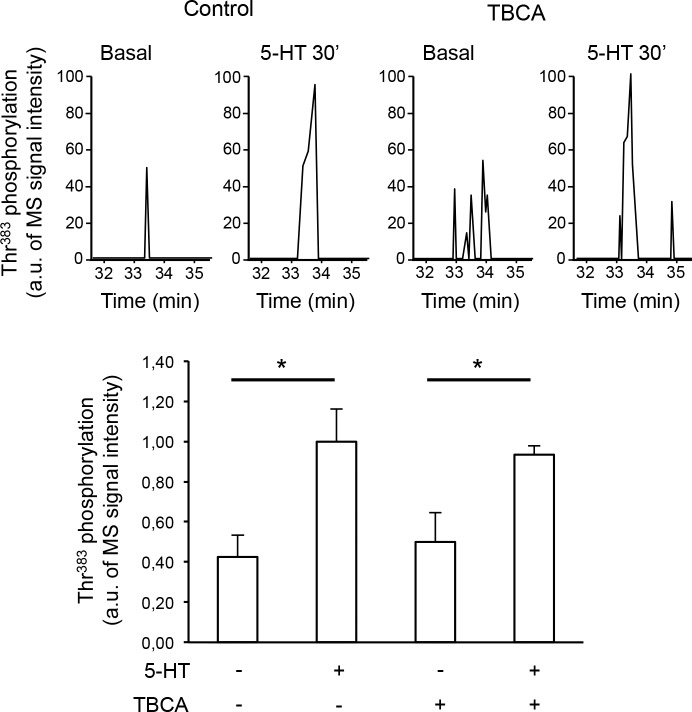
Figure 2. Role of MEK in the phosphorylation of β-arrestin2 at Thr383 elicited by 5-HT2C receptor stimulation.
(A) Mechanistic model of assembly of the 5-HT2C receptor/β-arrestin2/Erk module. Color code: receptor in orange, MEK in green, β-arrestin2 core in pale cyan and C-tail in cyan (the regions 351–384 and 394–419, which are not visible in 3D structure are represented by dashed lines, the region 385–393 is represented by spheres), Erk in dark red, Raf-1 RBD domain in pink. In this model, we hypothesize that Thr383 phosphorylation by MEK takes place within the assembled receptor/β-arrestin/Raf/MEK complex and results in a movement of β-arrestin2 unfolded 350–393 segment away from the first β-strand of β-arrestin, leaving space for further interaction with the receptor C-terminal domain (orange spheres) and recruitment of Erk, and its subsequent phosphorylation by MEK. For the clarity of the figure, the extremity of the β-arrestin C-tail is represented by spheres even in its unfolded state, although the real 3D structure is unknown. (B) Representative extracted ion chromatograms of the peptide in cells expressing 5-HT2C receptor, pretreated with either vehicle (control) or FR180204 (10 µM for 18 hr) or U0126 (5 µM for 30 min) or coexpressing MEK1 dominant-negative mutant (MEK1DN), and challenged with vehicle (Basal) or 5-HT (1 µM) for 30 min. The histogram represents the means ± SEM of the corresponding ion signal intensities (normalized to values in 5-HT-stimulated cells in Control condition) obtained in three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA: F(8,18) = 15.69, p<0.0001. ***p<0.001 vs. corresponding basal value. (C) YFP-tagged β-arrestin2 (wild-type or Thr383Ala mutant) purified from transfected HEK-293 cells was incubated with active MEK1 for 15 min at 37°C. When indicated, U0126 (5 µM) was included in the incubation medium. Thr383 phosphorylation was assessed by sequential immunoblotting with the antibody raised against phospho-Thr383 β-arrestin2 and the anti-β-arrestin2 antibody. Means ± SEM of results from four independent experiments are shown on the histogram. n.d.: not detectable. One-way ANOVA: F(2,9) = 352.2, p<0.0001. ***p<0.001 vs. immunoreactive signal in absence of MEK; §§§ p<0.001 vs. corresponding condition in absence of U0126.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.23777.010