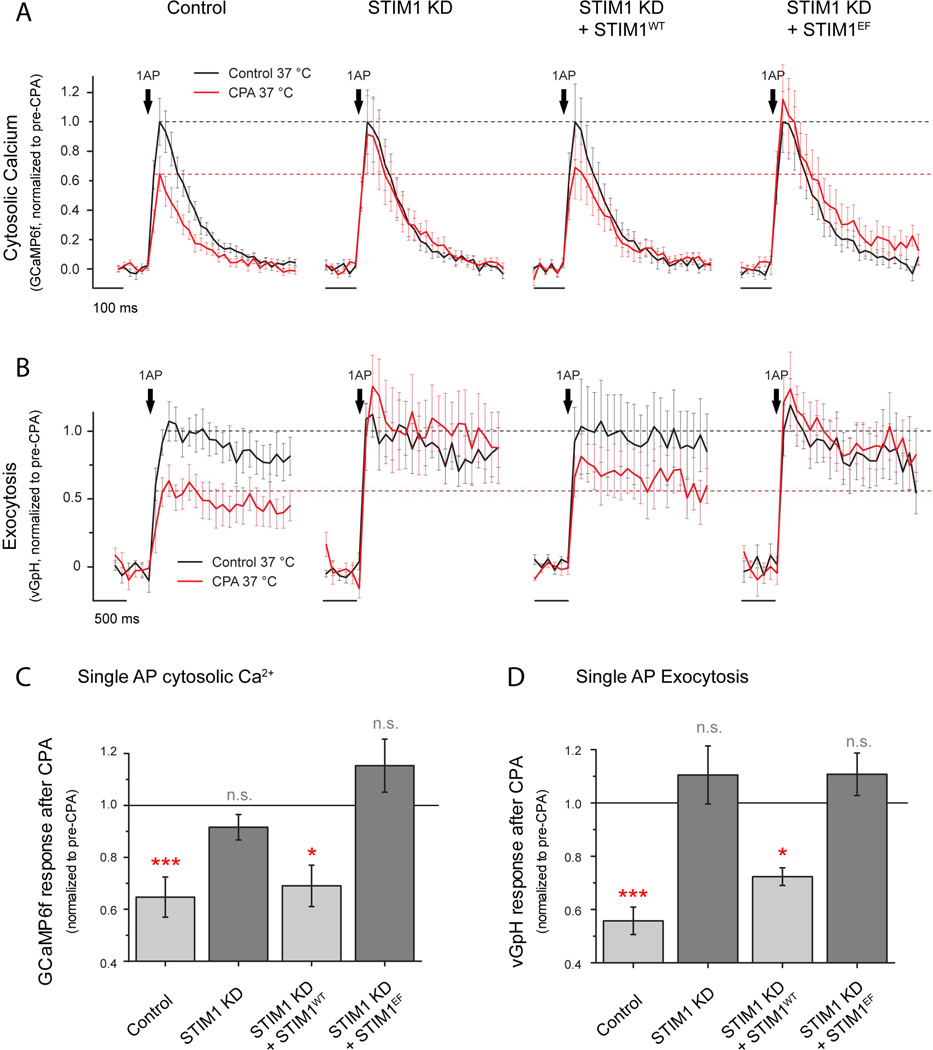
Figure 7. STIM1 regulates presynaptic function impairment induced by ER Ca2+ depletion.
(A-D) Single AP-driven cytosolic Ca2+ signals and exocytosis were measured using GCaMP6f or vG-pH, respectively. Single-AP stimulated signals were quantified in wild type neurons, STIM1 KD neurons, STIM1 KD neurons expressing an shRNA-resistant version of STIM1 (STIM1WT) or STIM1 KD neurons expressing an shRNA-resistant version of STIM1 that is insensitive to ER Ca2+ content due to EF-hand mutations (STIM1EF). Responses were quantified before (black) and after (red) CPA treatment. Black dashed lines represent average response before treatment whereas red dashed lines represent the effect quantified in wild type neurons for ease of comparison in the different conditions. (C-D) Differential effects of CPA are summarized by showing the remaining response after CPA treatment in each of the conditions. Solid black line indicates response before CPA treatment, normalized to 1 in each case. (C) Effects of CPA in single-AP-driven presynaptic Ca2+ signals, Control n=16, ***p=0.0016; STIM1 KD n=14, n.s. p=0.60; STIM1 KD + STIM1WT n=10, *p=0.02; STIM1 KD + STIM1EF n=10, n.s. p=0.14. (D) Effects of CPA in single-AP vG-pH peak responses, Control n=10, ***p=6.68·10−5; STIM1 KD n=7, n.s. p=0.22; STIM1 KD + STIM1WT n=7, *p=0.031; STIM1 KD + STIM1EF n=7, n.s. p=0.55. Statistics were analyzed using paired sample Student’s t-test.