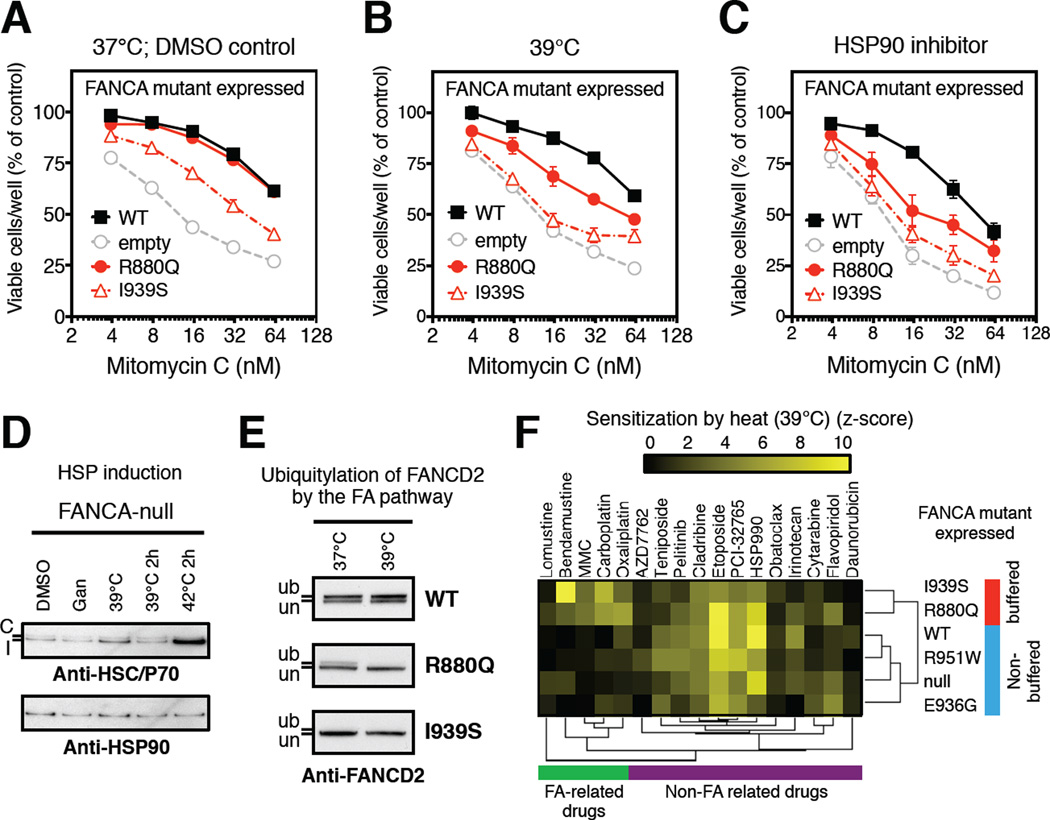
Figure 4. Exposure to febrile-range temperatures phenocopies low-level HSP90 inhibition.
(A–C) MMC sensitivity of FANCA-null GM6914 cell-lines expressing the indicated FANCA mutants recovering under normal conditions (DMSO control) (A), at a febrile-range temperature (39°C) (B), or in the presence of low-level HSP90 inhibition (ganetespib, 5 nM) (C). Data presented as mean ± SEM from 4 independent experiments; these experiments are distinct from those in Figure 3B–C.
(D) Effect of low-level HSP90 inhibition (Gan: ganetespib, 5 nM O/N) vs. exposure to febrile-range temperatures on HSP70 or HSP90 levels in FANCA-null (GM6914) cell. Cells underwent transient (39°C 2h or 42°C 2h; including 11-hour recovery at 37°C to allow for HSP induction; heat-shock protein) or prolonged overnight (39°C) exposure. Both constitutive (C, upper band, Anti-HSC70) and inducible (I, lower band, Anti-HSP70) forms of HSP70 are indicated, compared to HSP90, as determined by Western blotting with specific antibodies.
(E) Effects of low-level HSP90 inhibition (Gan: ganetespib, 5 nM vs. 39°C) on FANCD2 ubiquitylation in cells exposed to hydroxyurea (1 mM; 24 h). Samples from FANCA wild-type GM6914 cells were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against the indicated proteins. un indicates the unmodified FANCD2 protein, and ub the monoubiquitinated species.
(F) Mutant-specific chemo-sensitization by temperature increase to febrile-range (39°C). Hierarchical clustering of significant relative sensitization by febrile-range temperatures (z-score >2) of FANCA-null (GM6914) cells expressing the indicated FANCA mutants reveals two FANCA mutant clusters (HSP90-buffered mutants: red; non-buffered mutants: blue) on the basis of their differential sensitization to FA-related drugs (green cluster). Febrile-range temperature also sensitized cells to non-FA related drugs (purple cluster), but these effects were not mutant-specific. See also Figure S4