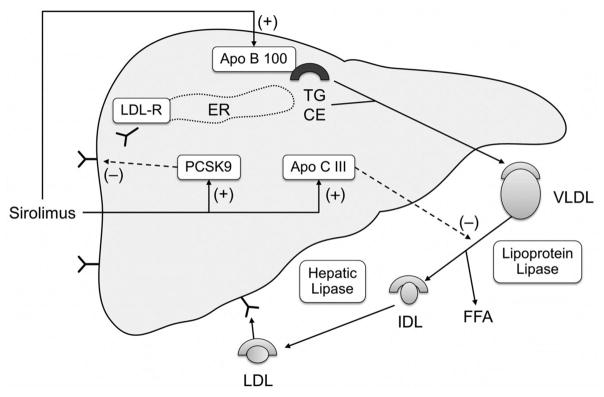
Figure 4.
(Central illustration). Mechanism of sirolimus-induced hyperlipidemia. Sirolimus increases the expression of Apo B100 leading to increased VLDL secretion. It also increases the expression of Apo CIII which inhibits lipoprotein lipase, and thus reduces hydrolysis and clearance of triglyceride rich lipoproteins. Both these effects contribute to hypertriglyceridemia. It also increases PCSK9 levels leading to decreased LDL receptor expression, and a resultant increase in LDL cholesterol levels. LDL-R, low density lipoprotein receptor; VLDL, very low density lipoprotein, FFA, free fatty acid; IDL, intermediate density lipoprotein; LDL, low density lipoprotein; ER endoplasmic reticulum; TG, triglyceride; CE, cholesterol ester.