Figure 1.
Detection of A-to-I Editing
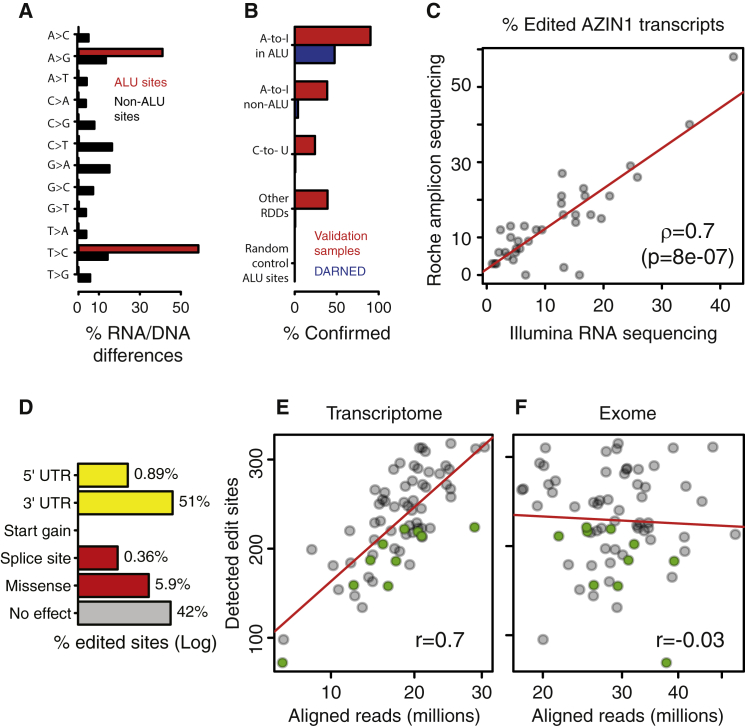
(A) Substitution frequencies of RDDs.
(B) Percentage of RDDs confirmed in the validation data set, n = 15 BCs (in red), and the DARNED database (in blue). The negative control set is composed of 1,000 sites selected at random positions in randomly selected Alu regions. Sites in immunoglobulin (Ig) hyper-variable regions were excluded; see the Supplemental Experimental Procedures.
(C) Each dot represents a sample for which the frequency of edited AZIN1 transcripts has been measured with Illumina full transcriptome sequencing (x axis) and Roche FLX amplicon sequencing (y axis). ρ denotes the Spearman’s correlation.
(D) Distribution of the 560 edited sites into functional categories.
(E and F) Number of detected Alu A-to-I sites as a function of transcriptome and exome coverages, respectively. Green dots represent tumor-matched normal samples.