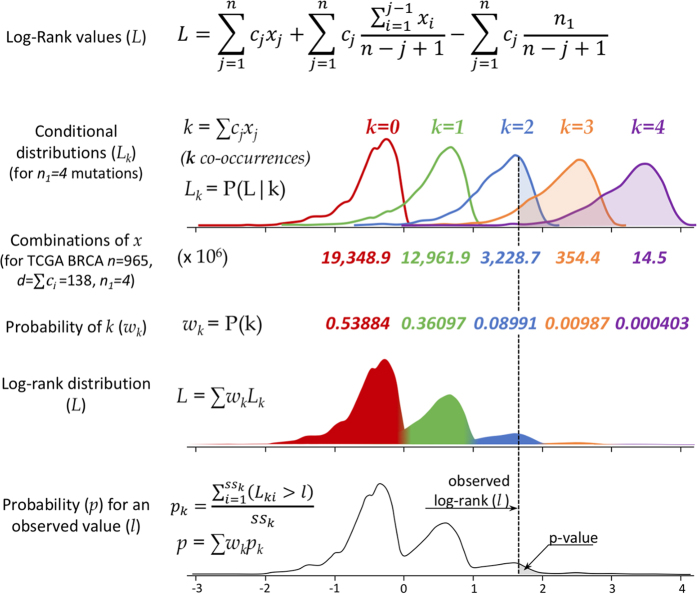
Figure 1. Overview of the VALORATE algorithm.
For a dataset having n samples, d deaths, and a gene having n1 sample mutations coded in the vector x of mutated subjects, the conditional distributions Lk are estimated by random sampling x over k, where k is the number of co-occurrences (events that are also mutated). The proportional weight wk of each Lk can be estimated by the contribution to the total number of combinations, which for a given k can be calculated by C(n − d, n1 − k)*C(d, k), where C is the combination function. The overall distribution is then estimated by a weighted sum on Lk. Finally, the p-value for an observed log-rank value in a mutated gene can be estimated by weighting the conditional p values over k.