Fig. (2).
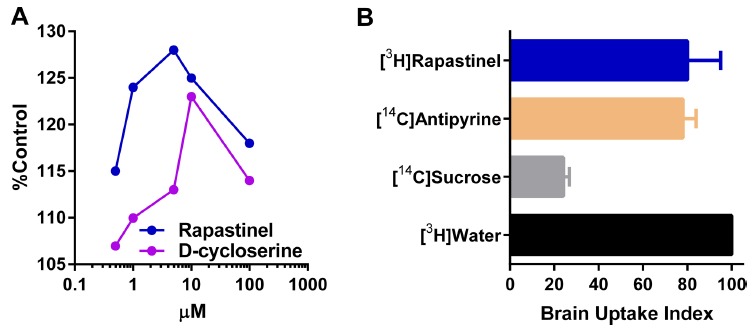
Rapastinel activates NMDA receptor activity and readily crosses the blood–brain barrier. (A) Comparison of Rapastinel NMDA receptor modulatory activity compared with D-cycloserine. NMDA receptor modulatory activity was measured by monitoring [3H]MK-801 binding in well washed rat forebrain membrane preps in the presence of glutamate but not glycine. Both Rapastinel and D-cycloserine showed an optimal increase in [3H]MK-801 binding in the range of 1-10 µM. Each data point represents the average of two experiments each done in triplicate (n=6) with the values for each data point varying by no more than 3-5%. Baseline MK-801 binding was 0.6 ± 0.06 pmol/mg protein. (B) Blood–brain-permeability studies were performed using [3H]-Rapastinel, along with the appropriate controls, was injected into rats IV and binding was measured in brain homogenates using liquid scintillation spectrometry. Using these methods a brain uptake index (Oldendorf, 1970) of 80 ± 15 was obtained suggesting that Rapastinel readily crossed the blood–brain barrier. Data were adapted with permission from [14].
