Fig. (8).
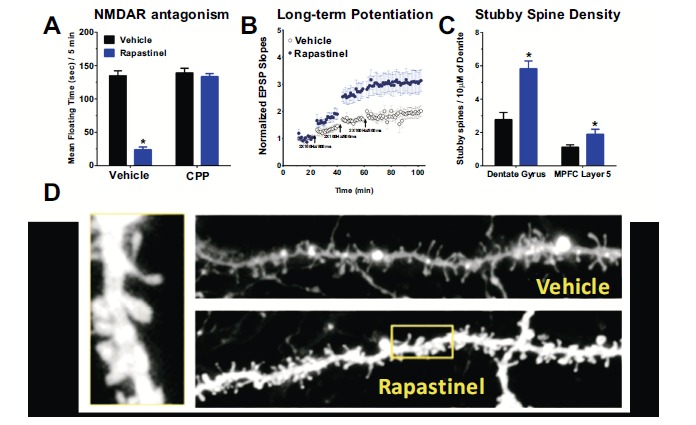
The therapeutic-like effects of Rapastinel are due to activation of NMDA receptor dependent synaptic plasticity. (A) The induction of the antidepressant-like effect of rapastinel is blocked by the NMDAR antagonist CPP. Mean (±SEM) floating time in the Porsolt forced swim test in 2-3 month old male SD rats pretreated with the NMDAR receptor antagonist CPP (10 mg/kg ip; or saline vehicle ip) 1 hr before rapastinel (3 mg/kg, IV) dosing and tested 1 hr post dosing with rapastinel. (B) A single in vivo dose of rapastinel (3 mg/kg iv; filled blue circles) in 2-3 month old male SD rats significantly enhanced the magnitude of long-term potentiation (LTP) of synaptic transmission compared to vehicle treated controls (open black circles), tested in vitro 24 hrs post-dosing at Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses after 1, 2 and 3 sub-maximal high-frequency stimulus trains (2x100Hz/800ms). (C) Rapastinel (3 mg/kg, IV; 24 hrs post-dosing) increased the density (spines / 10 µM of dendrite) of the most electrophysiologically active spine type (stubby spines) in the dentate gyrus (primary apical, 100-150 µM from the dendrite) or MPFC layer 5 tufts. (D) Representative laser-scanning confocal micrographs of layer 5 MPFC dendrites from rapastinel and vehicle treated animals. Data was adapted with permission from [30].
