Fig. (1).
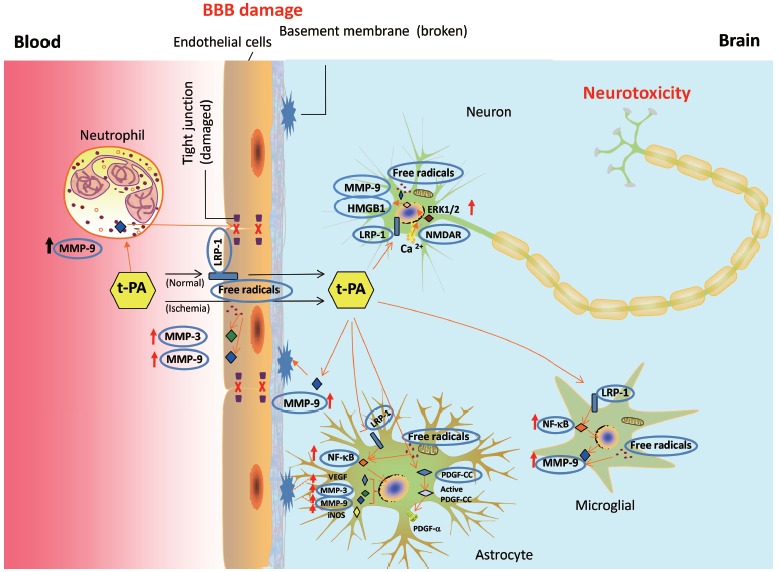
Mechanisms and molecular targets participate in tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA)-mediated BBB damage and neurotoxicity. T-PA acts on neutrophil, endothelial cells, astrocytes, microglials, and neurons to induce BBB damage and neurotoxicity. T-PA crosses BBB through LRP-1 dependent and independent pathways. LRP-1, NF-κB, MMPs, VEGF, HMGB1, and PDGF-CC are important targets involved in t-PA induced BBB damage and HT. LRP-1 and NMDAR are involved in t-PA induced neurotoxicity, mediating calcium influx and activation of ERK1/2. Free radicals are involved both in BBB damage and neurotoxicity possibly by upregulating MMPs. LRP-1: Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; MMP-9/3: Matrix metallopeptidase 9/3; NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; PDGF-CC: Platelet-derived growth factor CC; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells.
