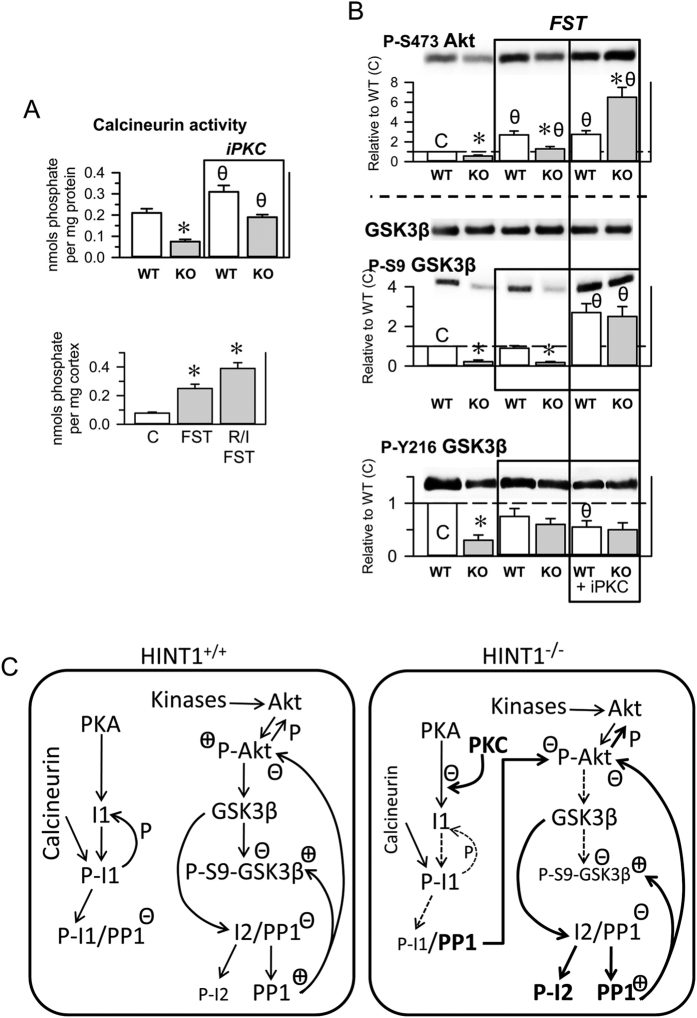
Figure 8. The effects of acute stress and PKC inhibition on calcineurin and Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway.
(A) Calcineurin enzymatic activity in prefrontal brain lysates from HINT1+/+ WT and HINT1−/− KO mice (n = 6). The effects of iPKC (upper panel) or stress (FST, R/I) (lower panel) on enzymatic activity were evaluated. *Significant difference from HINT1+/+ WT/C. θ Significant difference with respect to the corresponding group not receiving iPKC. ANOVA, Dunnett multiple comparisons vs control group, p < 0.05. (B) Mice that received vehicle or iPKC Gö7874 (1 nmol, icv) were immediately euthanized after the FST, and their frontal cortices were processed for molecular analysis. *For each situation, control, FST and FST + iPKC, the data of KO mice were compared with those of WT mice. θ The data from WT and KO mice (FST and FST + Gö7874) were compared with those of naïve control mice. For the statistical analysis and additional details, see Fig. 7 and the Methods section. (C) Diagram showing altered Akt/GSK3 signaling pathways in HINT1−/− mice. Key: PP1 (serine and threonine protein phosphatase 1), I1 (PP1 inhibitor 1), I2 (PP1 inhibitor 2), P- (phosphorylated forms), P-I1/PP1 (I1-dependent PP1 inhibition), I2/PP1 (I2-dependent PP1 inhibition), + and − (facilitation and inhibition of enzymatic activities). For details, see the main text.