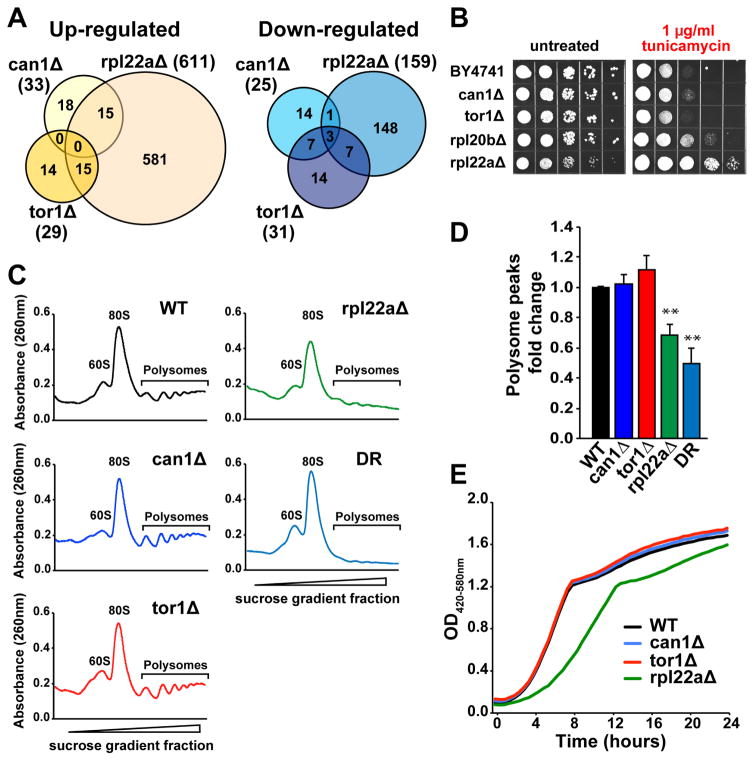
Figure 3. Deletion of CAN1 Promotes ER Stress Resistance and Activates Gcn4 without Reducing Global mRNA Translation.
(A) Genes translationally up- or down-regulated in can1Δ only partially overlap with rpl22aΔ and tor1Δ.
(B) Cells lacking CAN1 are resistant to tunicamycin. 10× serial dilutions of logarithmically growing cells were spotted on agar plates with indicated concentrations of tunicamycin and incubated for 48 h at 30°C.
(C–D) Polysome profiles of can1Δ, tor1Δ and rpl22aΔ mutants and cells under DR conditions indicate that neither CAN1 nor TOR1 deletion leads to inhibition of global mRNA translation. Representative polysome profiles (C) from three independent experiments are shown, and the area under polysome peaks was quantified using ImageJ software (D); **p<0.01. Error bars denote the standard error of the mean (SEM).
(E) Representative growth curves of can1Δ, tor1Δ and rpl22aΔ mutants. The doubling time for each strain is provided in Figure S2F, related to Figure 3.