Fig. 2.
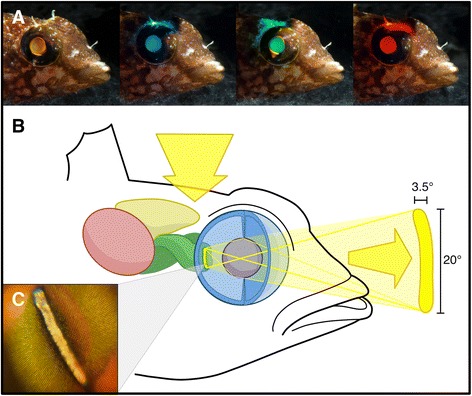
Laboratory demonstration and origin of ONT eyeshine. a Tripterygion delaisi illuminated dorsally with different spectra, illustrating that the ONT eyeshine is generated by skull illumination and based on transmission of the incident light (Additional file 2). b Schematic light path of ONT eyeshine in T. delaisi. Light, which enters through the dorsal head surface, passes through the anterior brain and extraocular ONs, exits through the optic disc, and is projected into the environment as a narrow beam of light. red: optic tectum; buff: telencephalon; green: optic nerves; blue: eye; purple: lens; yellow: ONT eyeshine light path. c View into the eye of T. delaisi through an endoscope (without internal light source) under the same illumination as in Awhite, showing the light-emitting, elongated optic disc (see also Additional file 3). A similar image can be seen directly with the human eye. Without small-aperture or micro-lens optics (e.g., endoscopes), the entire pupil seems to emit light since the optic disc’s image is blurred as a consequence of focusing on the outside of the fish with a wide aperture lens (as in a, taken with DSLR camera)
