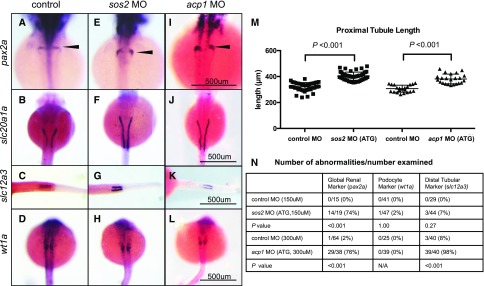
Figure 2.
sos2 and acp1 knockdowns result in defective kidney development. (A–D) Whole mount in situ hybridization in control embryos demonstrates normal expression of kidney markers, including pax2a (global kidney, A), slc20a1a (proximal tubules, B), and slc12a3 (distal tubules, C) at 48 hpf, and wt1a (podocytes, D) at 24 hpf. (E–L) sos2 and acp1 ATG morpholino (MO) knockdown embryos develop glomerular gene expression defects (E, I, arrowheads) and display elongated proximal tubules (F, J). Knockdown of acp1 shortened the distal tubules, whereas sos2 knockdown left distal tubule slc12a3 expression unaffected (G, K). No abnormalities in podocyte marker wt1a were observed for sos2 ATG- and acp1 ATG-MOs (H, L). (M) Quantitative assessment of proximal tubule length (slc20a1a expression) shows that proximal tubules are elongated in sos2 ATG- and acp1 ATG-MO injected embryos. t test used to calculate P values. (N) Table of observed abnormal embryos and total number examined by kidney markers pax2a, wt1a, and slc12a3, and MO-injected or control status. Fisher exact test used to calculate P values.