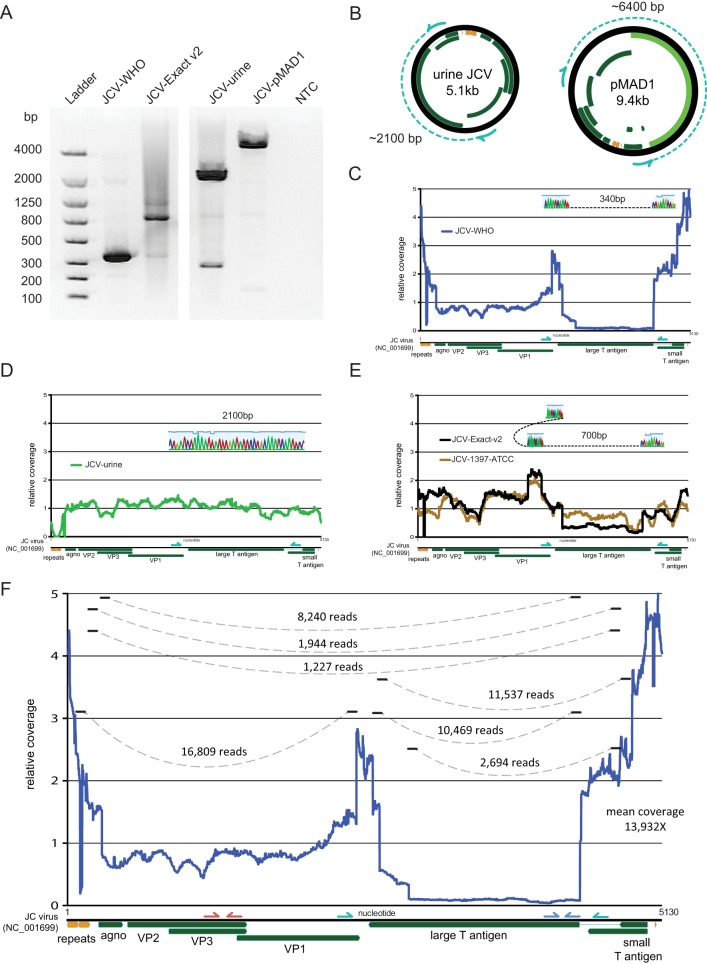
FIG 2.
Sanger confirmation of junction reads from next-generation sequencing data. (A) Gel electrophoresis of PCR products amplified with primers between nucleotides 2416 and 4543 based on the JC virus reference genome in NCBI (GenBank accession number NC_001699). NTC, no template control. (B) Expected PCR amplicons in control materials used in this study based on nucleotide distance. The JC virus plasmid pMAD1 contains a 4-kb backbone insert within this PCR amplicon. (C) The PCR amplicon of 340 bp recovered from the WHO standard demonstrates one of the large deletions in the T antigen region that was first identified by next-generation sequencing data. (D) The PCR amplicon of 2,100 bp demonstrates no deletion in the T antigen region in a JC virus from a clinical urine specimen. (E) The PCR amplicon of 700 bp demonstrates a complex rearrangement in the Exact v2 standard and JCV ATCC 1397 strain that was first identified by next-generation sequencing data. (F) Junctional reads with more than 5% allele frequency from the deep sequencing of the WHO JC virus standard are depicted.