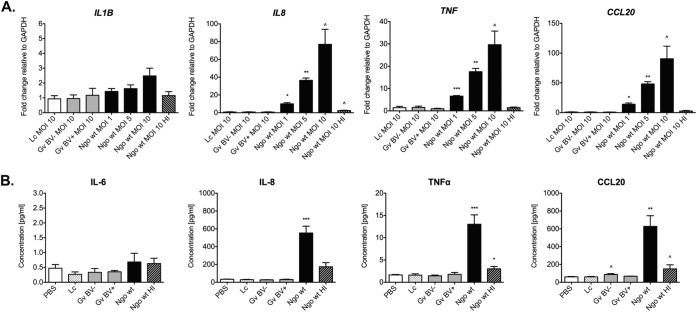
FIG 5.
Increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines following infection with N. gonorrhoeae but not with L. crispatus or G. vaginalis. Human EEC aggregates were infected with L. crispatus VPI-3199, G. vaginalis JCP8066 from a BV-negative woman, G. vaginalis JCP8151B from a BV-positive woman, or N. gonorrhoeae MS11 at the indicated MOIs. N. gonorrhoeae was heat inactivated (HI) at 55°C for 30 min. (A) The levels of expression of the IL-1B, IL-8, TNF, and CCL20 transcripts were determined by qRT-PCR using total RNA from lysed cells. mRNA levels were first normalized to the level of mRNA for the GAPDH gene and then compared to those for PBS-treated samples, and the fold change was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method. (B) The levels of secreted IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, and CCL20 in supernatants from the cell cultures infected at an MOI of 10 were measured by use of a BioPlex array. Data are shown as the means ± SDs from at least three independent experiments, each of which was performed in duplicate. Lc, L. crispatus VPI-3199; Gv BV−, G. vaginalis JCP8066 from a BV-negative woman; Gv BV+, G. vaginalis JCP8151B from a BV-positive woman; Ngo, N. gonorrhoeae MS11; wt, wild type. P values were calculated by an unpaired two-tailed Student t test. ^, P < 0.05; *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001.