FIG 9.
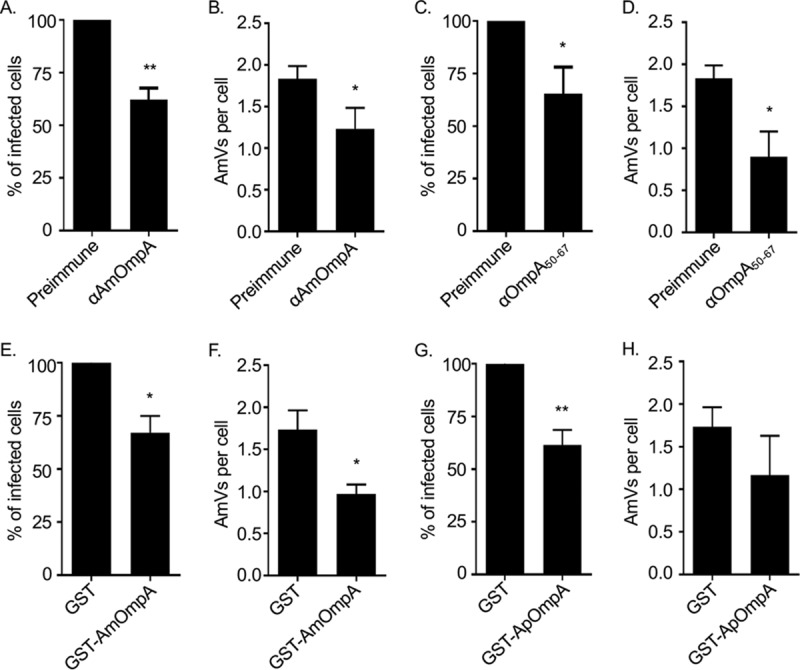
AmOmpA contributes to A. marginale infection of tick cells. (A to D) Antisera raised against AmOmpA and AmOmpA50–67 inhibit infection. A. marginale DC organisms were incubated with preimmune serum or antiserum specific for AmOmpA (A and B) or AmOmpA50–67 (C and D) for 1 h, followed by incubation with ISE6 cells in the continued presence of sera for 5 h. Unbound bacteria were removed and the infection was allowed to proceed for 72 h, after which the host cells were fixed and examined using immunofluorescence microscopy to determine the percentages of infected cells (A and C) and the number of AmVs per cell (B and D). (E to H) Recombinant AmOmpA and ApOmpA competitively inhibit A. marginale infection of tick cells. ISE6 cells were incubated with GST alone (E to H), GST-AmOmpA (E and F), or GST-ApOmpA (G and H) for 1 h. A. marginale DC organisms were then added and incubated with the cells in the presence of recombinant protein for 5 h. After washing to remove unbound bacteria, host cells were incubated for 72 h and subsequently examined by immunofluorescence microscopy to determine the percentage of infected cells (E and G) and AmVs per cell (F and H). Results are the means ± SD from triplicate samples and are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. Statistically significant (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005) values are indicated.
