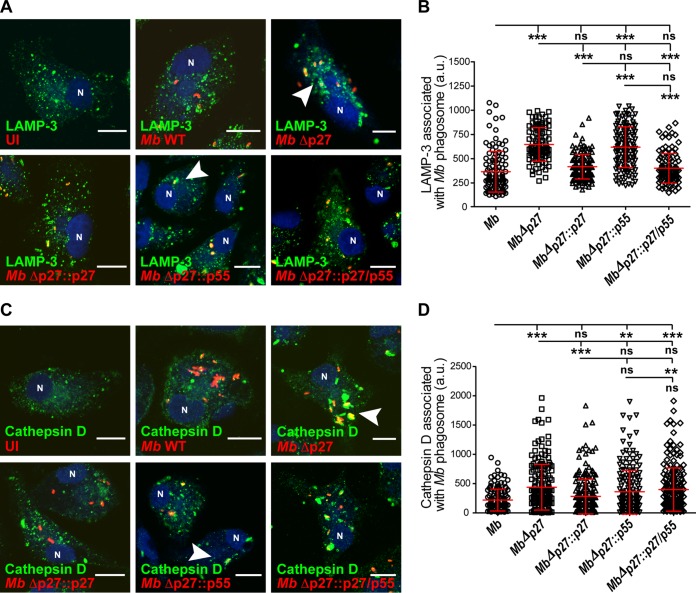
FIG 2.
Mutation of the p27-p55 operon is required for phagosome maturation arrest. (A) BMDMs were infected with the different M. bovis strains labeled with rhodamine (red) during 1 h of uptake and 2 h of chase. The cells were fixed and subjected to indirect immunofluorescence with an antibody against LAMP-3 (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole [blue]). The arrowheads in the images show the mycobacterial phagosomes. Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) Quantitation of LAMP-3 associated with M. bovis phagosomes. Results for M. bovis wild type (○), mutant MbΔp27 (□), and complemented strains MbΔp27::p27 (△), MbΔp27::p55 (▽), and MbΔp27::p27/p55 (♢) are shown. (C) BMDMs were infected with the different M. bovis strains labeled with rhodamine (red) for 1 h of uptake and 2 h of chase. The cells were fixed and subjected to indirect immunofluorescence with an antibody against cathepsin D (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). The arrowheads in the merge images show the mycobacterial phagosomes. Scale bars, 10 μm. (D) Quantitation of cathepsin D associated with M. bovis phagosomes. Results for M. bovis wild type (○), mutant MbΔp27 (□), and complemented strains MbΔp27::p27 (△), MbΔp27::p55 (▽), and MbΔp27::p27/p55 (♢) are shown. The cells were analyzed by confocal microscopy and quantified using Fiji software. The data represent the means ± the standard errors of the mean (SEM) of three independent experiments. The values at each point were significantly different among strains, as determined by ANOVA and Tukey's multiple-comparison tests. The asterisks indicate significance: ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; and *, P < 0.05. ns, not statistically significant.