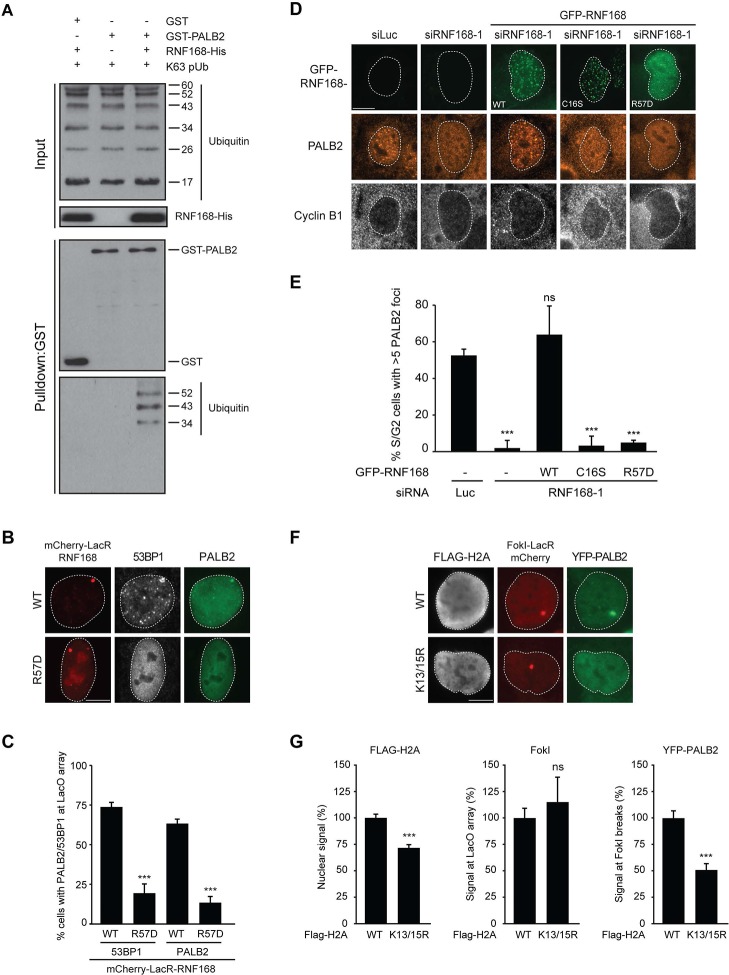
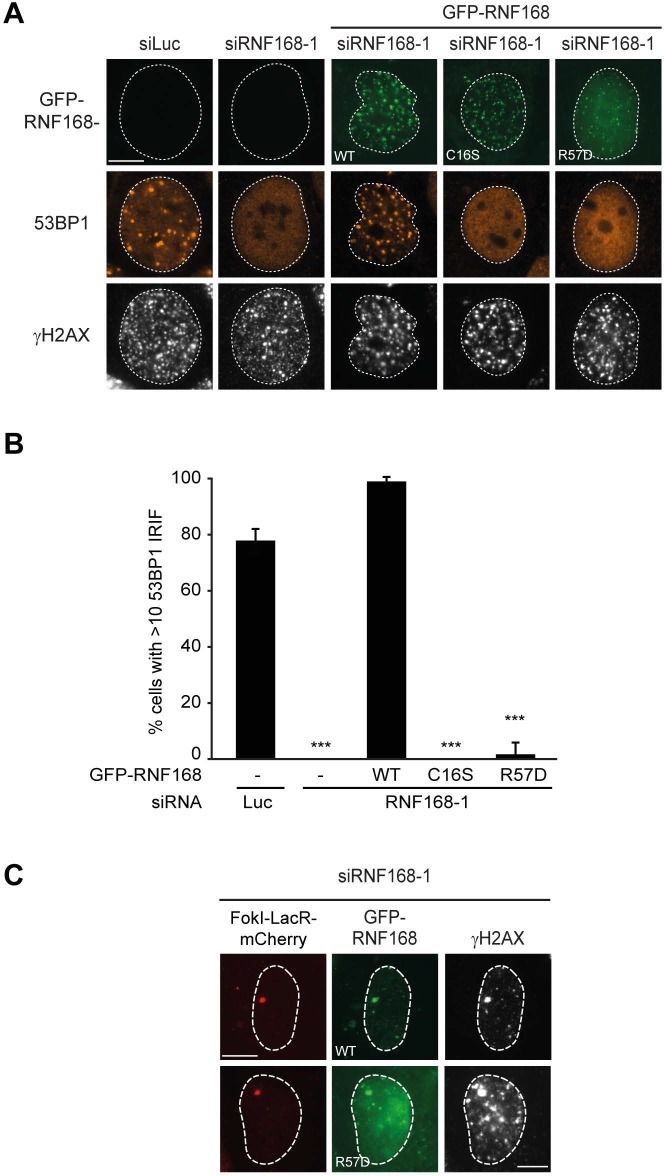
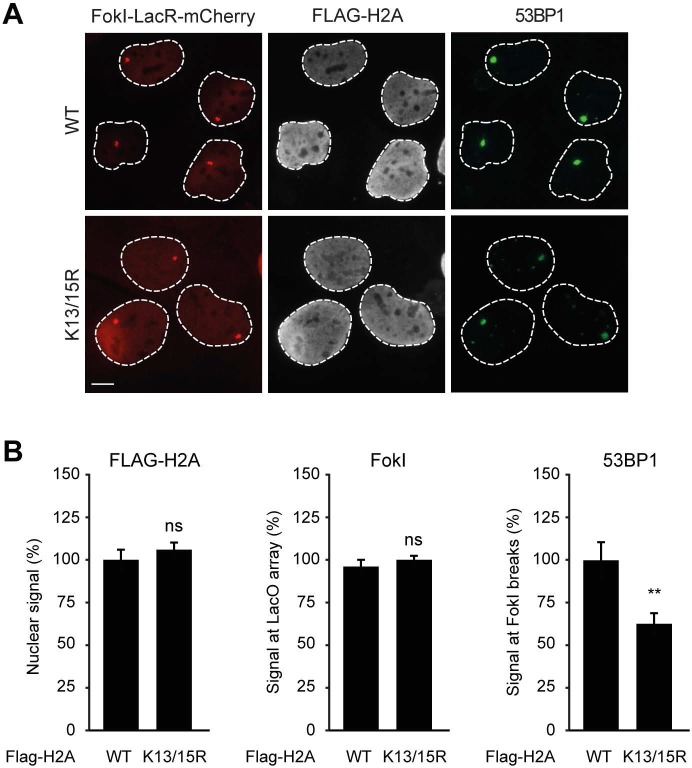
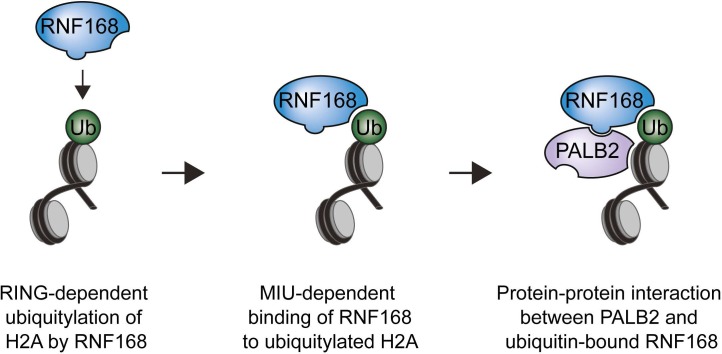
Figure 7. PALB2 associates with K63-polyubiquitin chains via RNF168.
(A) GST pulldowns to assess the binding of GST-PALB2 or GST-alone to K63 polyubiquitin (pUb) chains in the presence or absence of His-RNF168. Blots were probed for GST, ubiquitin and His. (B) Recruitment of 53BP1 (white) and YFP-PALB2 (green) upon tethering of the indicated mCherry-LacR-RNF168 variants (red) to a genomic LacO array in U2OS 2-6-3 cells. Indicated significance is compared to WT for each staining. (C) Quantification of B. (D) PALB2 IRIF formation (orange) in cyclin B1-positive U2OS cells (white) transfected with the indicated siRNAs and siRNA-resistant GFP-tagged RNF168 cDNAs (green). (E) Quantification of D. Indicated significance is compared to siLuc. (F) Recruitment of YFP-PALB2 (green) to DSBs induced by FokI-mCherry-LacR at a LacO array (red) in U2OS 2–6-5 cells expressing the indicated FLAG-H2A constructs (white). (G) Quantification of F. Indicated significance is compared to WT for each staining. Quantified data are represented as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 3), except in E where n = 4. Scale bar = 5 µm.