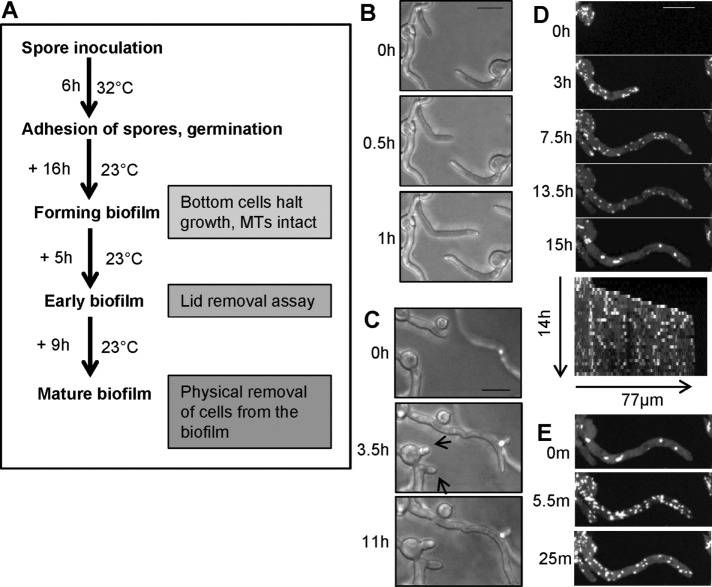
FIGURE 2:
During early stages of A. nidulans biofilm formation, cells stop growing and then undergo distinctive changes in their EB1-GFP behavior reflecting MT depolymerization. (A) Schematic representation of growth conditions used for examining EB1-GFP localization during different stages of biofilm formation. (B) During the initial growth phase of biofilm formation (strain SO1563), cells can change their growth direction when growing toward each other. (C) Cells then stop growing (arrows) as they become further crowded. (D) The montage and kymograph show that after cells stop growing, they initially maintain EB1-GFP comets, but then EB1-GFP starts to disperse and form immobile bars and foci (15 h). (E) Surprisingly, EB1-GFP relocates back to comets within minutes of removal of culture dish lid. Cells were initially grown at 32°C for 6 h, followed by growth for 10, 9, 6, and 21 h at 23 ± 2°C for imaging in B–E, respectively. Scale bar, 10 µm.