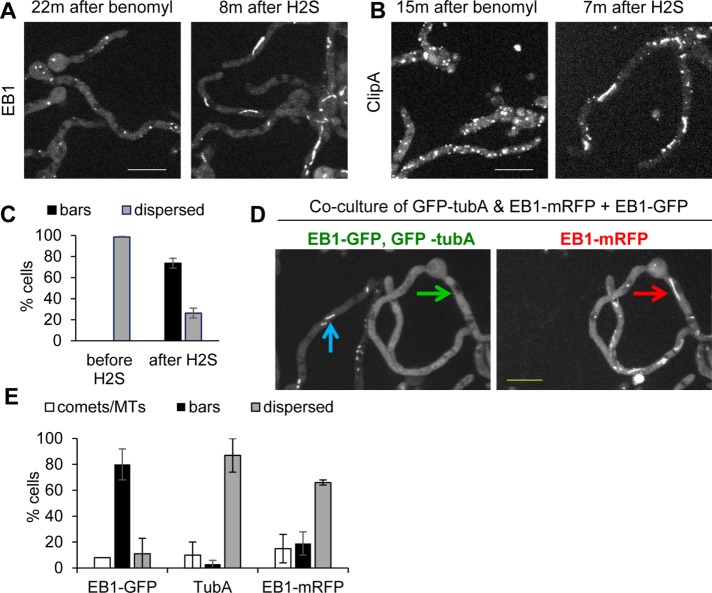
FIGURE 8:
EB1-GFP bars may not represent MT-based structures. (A) Benomyl treatment causes EB1-GFP (strain NS326) dispersal from comets, and subsequent NaHS addition then promotes EB1-GFP bar formation (Supplemental Video S14). (B) As also shown in Supplemental Figure S2, benomyl causes ClipA-GFP (strain NS141) to locate at immobile foci, but ClipA still relocates to bars upon treatment with NaHS (Supplemental Video S15). (C) Quantitation (mean ± SE) for EB1-GFP in benomyl-treated cells before and after NaHS treatment. The experiment was performed three times with 65 cells. (D) Coculture of strains expressing EB1-GFP (strain SO1563) and GFP-TubA and EB1-mRFP (strain NS133) during biofilm formation shows that when the majority of EB1-GFP cells display bars (blue arrow), none of the GFP-TubA locates to bars (green arrow). Within the same cell, at the time EB1-mRFP locates to bars (red arrow), GFP-tubA does not (green arrow). (E) Quantitation (mean ± SE) of EB1-GFP, GFP-TubA, and EB1-mRFP location to comets/MTs or bars or dispersed during biofilm formation. The experiment was performed twice with 122 cells. Scale bar, 10 µm.