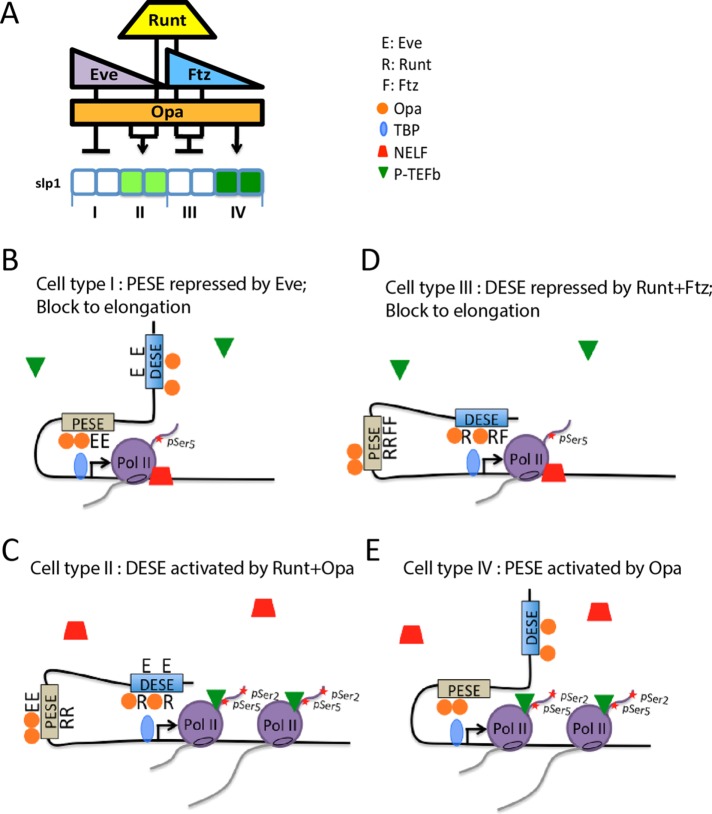
FIGURE 6:
Context-dependent regulation of slp1 transcription. (A) Schematic summarizing slp1 regulation in four different cellular contexts as also depicted in Figure 1A. The key to the right shows symbols representing the different pair-rule transcription factors, TBP, NELF, and P-TEFb in cartoons of proposed enhancer-promoter interactions in these different contexts. (B) In type I cells, PESE interacts with the promoter to recruit TBP, Pol II, and other PIC components to the promoter, and transcription is initiated. However, Eve inhibits P-TEFb recruitment, thereby blocking Pol II release and resulting in a NELF-associated paused Pol II complex. (C) In type II cells, Runt prevents PESE from interacting with the slp1 promoter. Instead, DESE mediates activation by Runt and Opa by increasing P-TEFb recruitment, pSer-2 modification of the Pol II CTD, and a release into productive transcription elongation that results in production of the odd-numbered slp1 stripes. (D) DESE also interacts with the promoter in type III cells, but the combination of Runt and Ftz inhibits P-TEFb recruitment, resulting in a paused Pol II complex and slp1 repression. (E) In type IV cells, the absence of Runt allows PESE to interact with the promoter, recruit Pol II, and promote transcription initiation. The absence of Eve allows P-TEFb recruitment, CTD Ser-2 phosphorylation, and Pol II release into productive transcription elongation, which results in production of the even-numbered stripes of slp1 expression.