Figure 1.
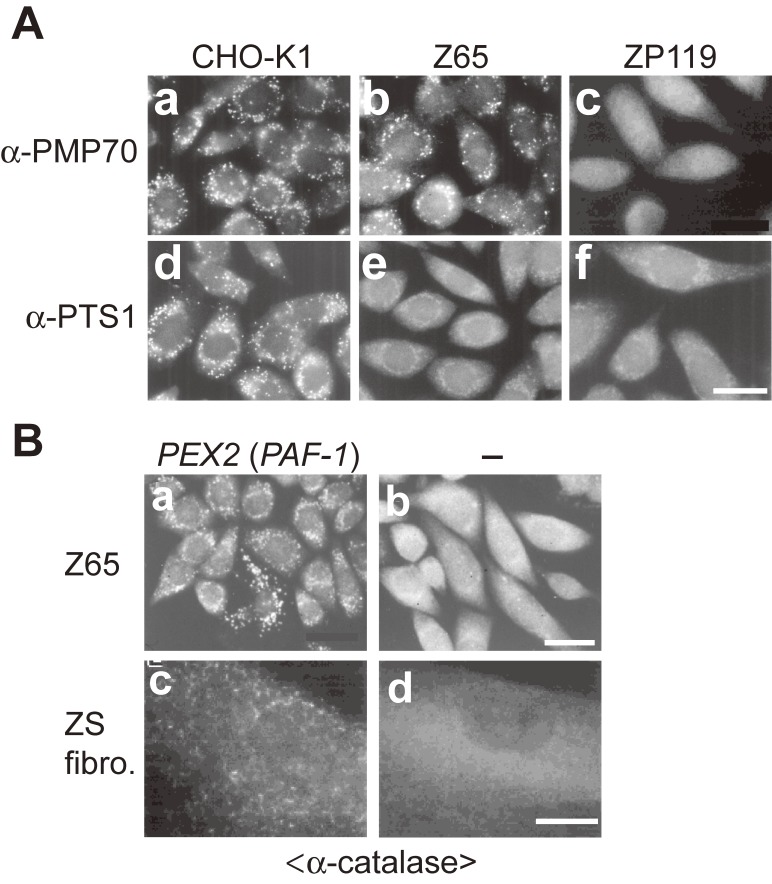
Morphology of peroxisomes in CHO cell mutants defective in peroxisome biogenesis and pathogenic gene cloning of PBDs. (A) CHO cells are stained with antibodies to PMP70 (a-c) and PTS1 (d-f). Cells are as indicated at the top. Scale bar, 20 µm. pex2 Z65 contains PMP70-positive peroxisomal remnants, whereas pex19 ZP119 is absent from such peroxisome ghosts, indicative of the defect of membrane protein import. PTS1 proteins are discernible in the cytosol in pex2 Z65 and pex19 ZP119 cells, in contrast to the wild-type CHO-K1 cells where PTS1 proteins are in peroxisomes. (B) Cloning of pathogenic gene responsible for PBD. Peroxisome-restoring PEX genes were isolated by functional phenotype-complementation assay using CHO mutants. Restoration of peroxisomes was searched by transfection of rat liver cDNA library (a) in Z65 (b). Transformed cells positive in catalase import contained PEX2 (formerly PAF-1). In fibroblasts from a patient with ZS of CG10 (d), expression of PEX2 restored the impaired import of catalase (c). Scale bar, 20 µm (a and b); 30 µm (c and d).