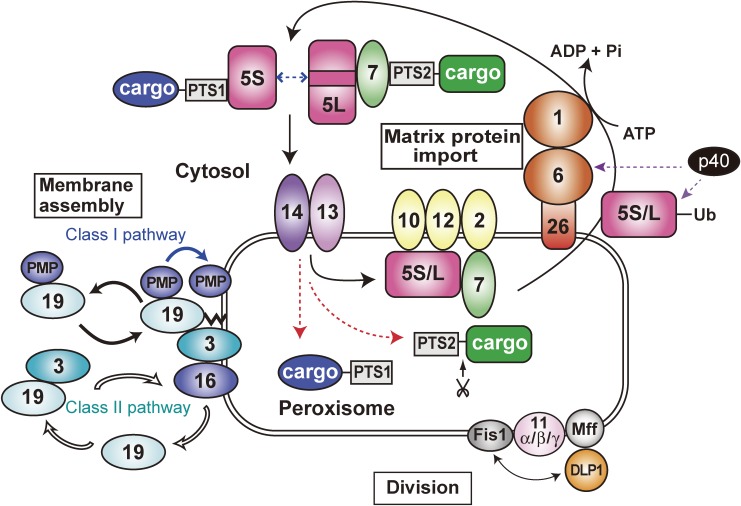
Figure 2.
A schematic view of peroxisome biogenesis in mammalian cells. The subcellular localization and molecular characteristics of peroxins are shown. Peroxins are classified into three groups: 1) peroxins including Pex3p, Pex16p and Pex19p that are responsible for peroxisome membrane assembly via classes I and II pathways required for matrix protein import; 2) those required for matrix protein import; 3) those such as three forms of Pex11p, Pex11pα, Pex11pβ, and Pex11pγ, apparently involved in peroxisome division where DLP1, Mff, and Fis1 coordinately function. PTS1 and PTS2 matrix proteins are recognized by Pex5p and Pex7p, respectively, in the cytoplasm. Two isoforms, Pex5pS and Pex5pL with an internal 37-amino-acid insertion, of Pex5p are identified in mammals. PTS1 proteins are transported by homo- and hetero-oligomers of Pex5pS and Pex5pL to peroxisomes, where Pex14p functions as a convergent, initial docking site of the ‘protein import machinery’ translocon. Pex5pL directly interacts with the PTS2 receptor, Pex7p, carrying its cargo PTS2 protein in the cytosol and translocates the Pex7p-PTS2 protein complex to Pex14p. PTS1 and PTS2 proteins are then released at the inner surface and/or inside of peroxisomes, downstream Pex14p and upstream Pex13p. Pex5p and Pex7p subsequently translocate to other translocon constituents, named translocation complex consisting of the RING peroxins, Pex2p, Pex10p, and Pex12p. Both Pex5p and Pex7p finally shuttle back to the cytosol. At the terminal step of the matrix protein import reaction, Pex1p and Pex6p of the AAA family catalyze the export of Pex5p, where Cys-monoubiquitination of Pex5p is a prerequisite to the Pex5p exit. Moreover, a cytosolic factor, AWP1/ZFAND6 (p40), is involved in the export of Ub-Pex5p in mammals.