Figure 3.
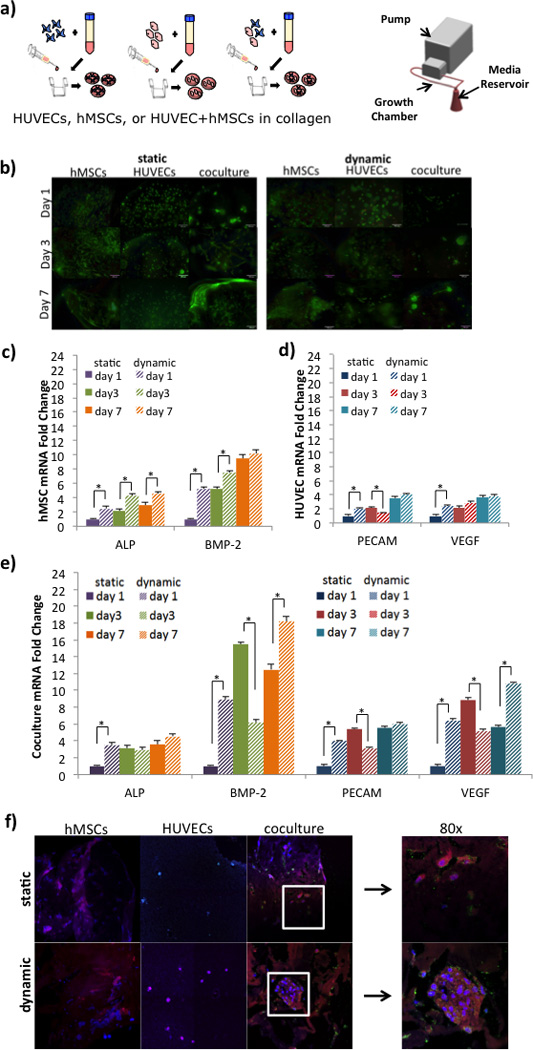
Effect of Dynamic Culture on hMSCs and HUVEC coculture. A) Experimental setup of cell encapsulation groups: hMSCs in collagen, HUVECs in collagen, or hMSCs and HUVECs in collagen. Cell-seeded scaffolds were cultured in static well plates or in the TPS bioreactor under dynamic flow conditions. B) E) Fluorescence viability images of hMSCs labeled with live (green) and dead (red) stain on 3D collagen scaffolds after 1, 3, or 7 days of static or dynamic culture. Scale bar represents 100 µm. C) Gene expression of ALP and BMP-2 in hMSCs monocultured in static (solid bars) or dynamic (striped bars). Overall, dynamic coculture resulted in the highest expression of ALP and BMP-2 expression by day 7. D) Gene expression of PECAM and VEGF in HUVEC monocultured in static (solid bars) or dynamic (striped bars). Overall, dynamic coculture resulted in the highest expression of PECAM and VEGF expression by day 7. E) Gene expression of ALP, BMP-2, PECAM, and VEGF in hMSC and HUVEC cocultured in static (solid bars) or dynamic (striped bars). Overall, the synergistic effect of coculture and dynamic coculture resulted in the highest expression of all four markers by day 7. The symbol ‘*’ indicates statistical significance within groups at a timepoint (p<0.05). F) Immunofluorescence staining of hMSCs, HUVECs, and coculture in static and dynamic. hMSCs were stained for BMP-2 (pink/red), counterstained with DAPI (blue). HUVECs were stained for CD31 (green), VEGF (red), and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Cocultured samples were stained for BMP-2 (pink/red), CD31 (green), and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Images were taken at 40× with an additional 2× zoom (right panel).
