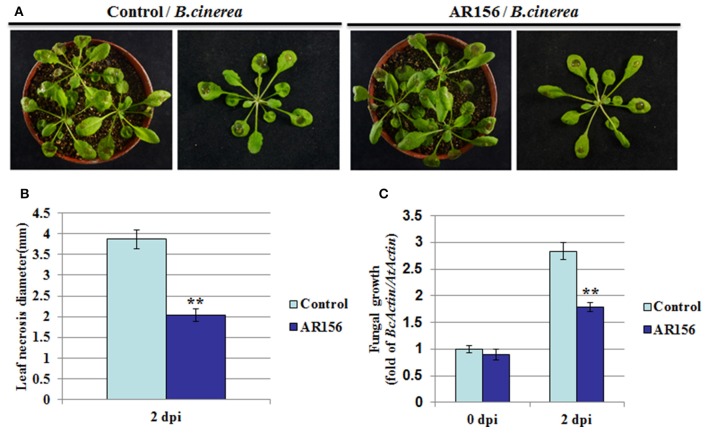
Figure 1.
B. cereus AR156 induces an effective ISR against B. cinerea infection. Arabidopsis Col-0 plants are drench-applied with AR156 at 5 × 108 CFU/ml or 0.85% NaCl (Control). Control-or AR156-treated plants (7 days) are inoculated by depositing a 10 ul droplet of B. cinerea spores (1 × 106 spores/ml) on each side of the midvein. (A) Disease symptoms observation and photo talking were made 2 days post infection (dpi). (B) Leaf necrosis development was evaluated at 2 dpi by measuring the average necrosis diameter on five leaves per plants for 10 plants (Col-0). (C) In planta growth of B. cinerea. Measurement of fungal growth was carried out by simultaneous quantification of the expression levels of B. cinerea Actin gene (BcActin) and the Arabidopsis Actin gene (AtActin). Relative fungal growth was determined by ratios of BcActin/AtActin. A Student's t-test was used to determine significant differences between the AR156-treated sample and the control (**P < 0.01). The means values ± SD (n = 12) from one representative experiment among three independent repeats are shown.