Figure 2.
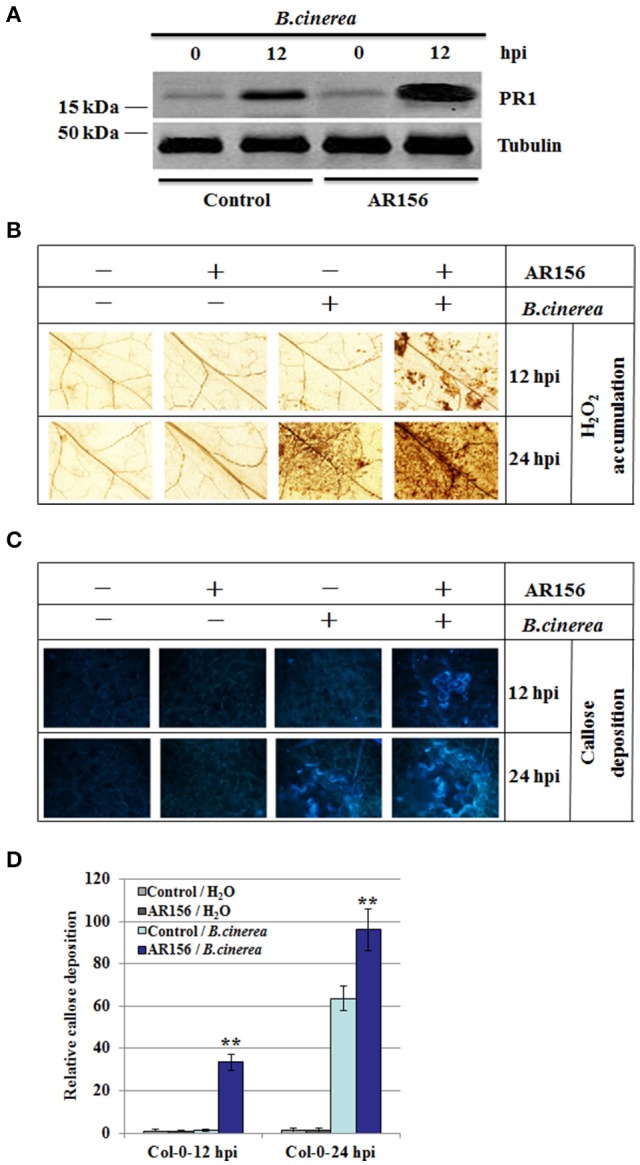
AR156 pretreatment induces PR1 protein expression, H2O2 accumulation and callose deposition in systemic leaves infected with B. cinerea Arabidopsis Col-0 plants were infected by B. cinerea spore suspension (1 × 106 spores/ml), and the leaves were collected at 12 hpi and 24 hpi, respectively. (A) PR1 was detected by an antibody specifically recognizes PR1; Tubulin was used as an equal loading control. (B–D) ROS accumulation (B) and callose deposition (C) were detected in plants with AR156- or control-pretreatment followed by B. cinerea or mock infection (Solution). ROS accumulation was detected by DAB staining; Callose deposition were observed under light and epifluorescence microscopes with a UV excitation filter. Relative callose quantities in droplet inoculated leaves of 4-week-old plants. Callose was quantified from digital microscopy photographs (D). Shown are mean areas of callose per leaf relative to total leaf area ± SD (n = 24). A Student's t-test was used to determine significant differences between the AR156-treated sample and the control (**P < 0.01). Similar results were obtained in three independent repeats.
