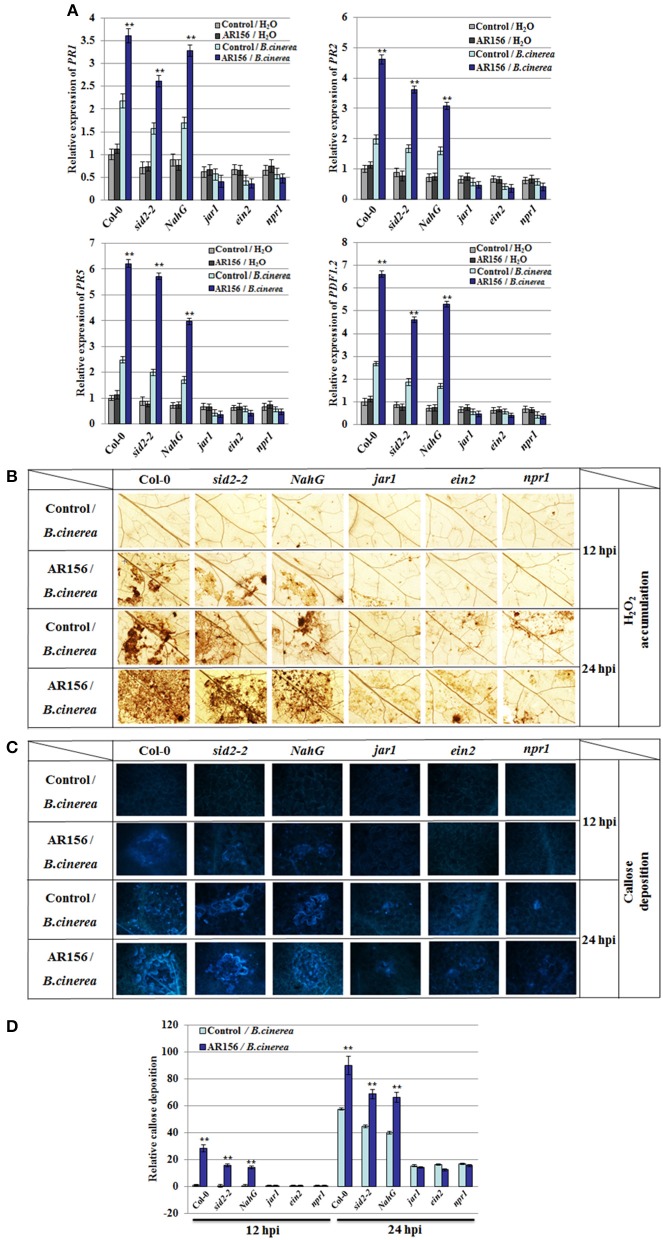
Figure 4.
Altered defense-related gene expression, H2O2 accumulation and callose deposition in Col-0, sid2-2, NahG, jar1, ein2, and npr1 mutant plants after B. cinerea infection. Four week old plants were infected with spore suspension of B. cinerea and leaf samples were taken 12, 24, and 48 hpi, respectively. (A) Expression of defense-related genes after B. cinerea infection. Expression of defense genes were analyzed by qRT-PCR and normalized with the value of AtActin, which is assigned to 1. Data are presented as the means ± SD from three independent experiments and different letters above the columns represent statistically significant differences (p < 0.01) between Col-0, sid2-2, NahG, jar1, ein2 and npr1 mutant plants. In situ detection of accumulation of H2O2 (B) and callose deposition (C, D) after inoculation with B. cinerea. Accumulation of H2O2 and callose deposition in leaves were detected by DAB staining and aniline blue staining, respectively. Relative callose quantities in droplet inoculated leaves of 4-week-old plants. Callose was quantified from digital microscopy photographs. Shown are mean areas of callose per leaf relative to total leaf area ± SD (n = 24). A Student's t-test was used to determine significant differences between the AR156-treated sample and the control (**P < 0.01).