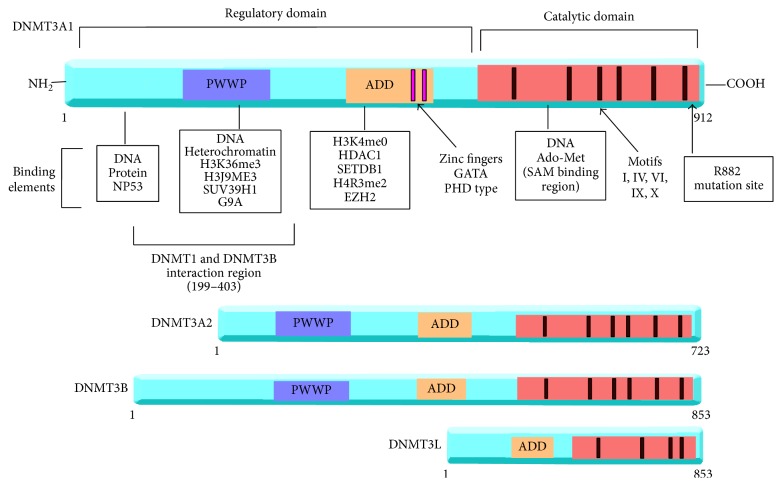
Figure 2.
Structure of DNMT3A splice isoforms, DNMT3B, and DNMT3L. Shown here is the structure of the DNMT3 enzymes. The ADD domain is related to the PHD- (plant homeodomain-) like regulator ATRX and has strong interactions with histones, which is thought to enhance its methylation activity. Meanwhile PWWP domain (Pro-Trp-Trp-Pro) is found to interact with DNA and heterochromatin to help carry out its function, among other proteins. The catalytic domain of the enzyme has motifs conserved across the isoforms. Motifs I are cofactor binding while motifs VIII and IX are for DNA binding and methylation activity at motifs IV, VI, and VIII. The main difference between the two splice isoforms of DNMT3A1 and DNMT3A2 is the extra DNA binding domain located at the amino terminal of DNMT3A1. Other DNMT enzymes are also able to interact with DNMT3A. One common mutation site shown here is R882 residue. This is a hotspot for mutations in haematological malignancy and preleukaemic conditions. Not depicted here are the splice isoforms for DNMT3B and the structure of DNMT1. Adapted from Yang et al. [2].