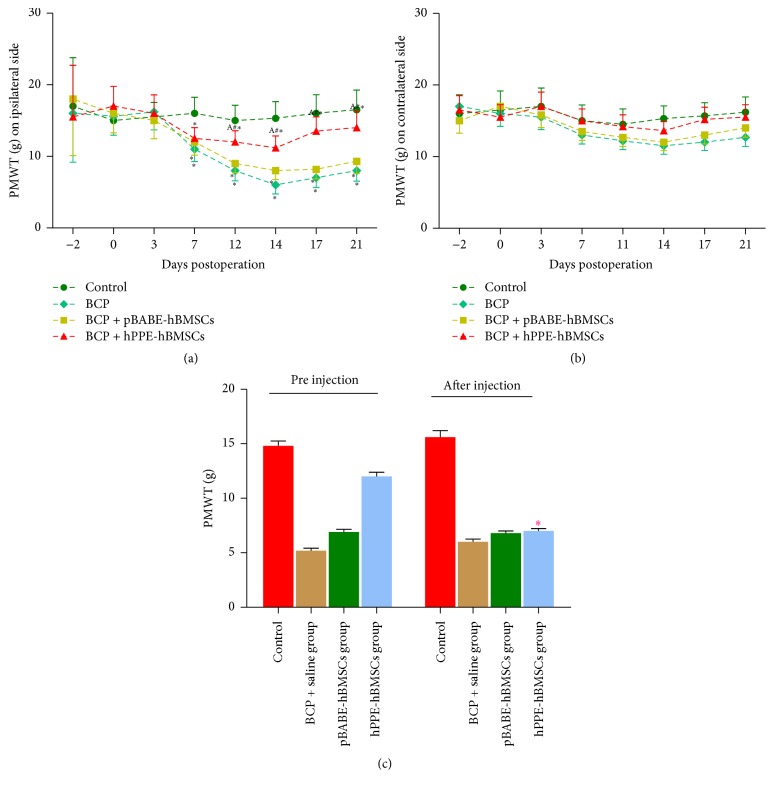
Figure 5.
(a) Comparison of the paw mechanical withdrawal threshold (PMWT) indicating mechanical hyperalgesia changes on the ipsilateral side during the time course of Walker 256 cell incursion. Mechanical allodynia occurred starting on day 7, peaked on day 14, and then weakened until day 21. A significant decrease in PMWT was shown in the BCP, BCP + pBABE-hBMSCs, and BCP + hPPE-hBMSCs groups compared with the control group (P < 0.05), and treatment with hPPE-hBMSCs impaired the decrease in PMWT caused by cell administration. PMWT in the hPPE-hBMSC group was significantly higher than that in the BCP and pBABE-hBMSC groups (P < 0.05). ∗P < 0.05 versus the control group; #P < 0.05 versus the BCP group; AP < 0.05 versus the pBABE-hBMSC group. BCP, bone cancer pain; hPPE, human proenkephalin; pBABE, a retroviral vector; hBMSCs, human bone marrow stem cells; Control, the control group; BCP, the BCP + saline group; pBABE-hBMSCs, the pBABE-hBMSC group; hPPE-hBMSCs, the hPPE-hBMSCs group. n = 6. (b) Comparison of the paw mechanical withdrawal threshold (PMWT) indicating mechanical hyperalgesia changes on the ipsilateral side during the time course of Walker 256 cell incursion. There were no significant differences among the groups (P > 0.05). BCP, bone cancer pain; hPPE, human proenkephalin; pBABE, a retroviral vector; hBMSCs, human bone marrow stem cells; Control, the control group; BCP, the BCP + saline group; pBABE-hBMSCs, the pBABE-hBMSC group; hPPE-hBMSCs, the hPPE-hBMSC group, n = 6. (c) Naloxone was used to reverse the antiallodynia effect of met-enkephalin in bone cancer rats. The results showed that paw mechanical withdrawal threshold (PMWT) was significantly reduced after naloxone administration (P < 0.05). ∗P < 0.05 versus PMWT of the hPPE-hBMSCs group before injection. BCP, bone cancer pain; hPPE, human proenkephalin; pBABE, a retroviral vector; hBMSCs, human bone marrow stem cells. n = 6.